The ancestor of SARS-CoV-2’s Wuhan strain was circulating in late October 2019
By
May 7 2021
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was first reported in a case from Wuhan, China, in December 2019, and subsequently became the cause of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic that is ravaging the world today. A new study in the journal
tracks its variants all over the world since the onset of the pandemic.
Genomic sequencing has occurred using hundreds of thousands of viral genomic samples. The researchers used the best of these sequences to reveal how the virus has mutated and changed in different periods and regions of the pandemic.
Study: . Image Credit: vchal / Shutterstock
Using a new approach
Conventional methods have not produced a reliable history of the emergence of this virus for several reasons. These include the numerous widespread sequencing errors in the available sequences, small degree of sequence divergence, and the fact that there are few sites that help to understand the descent of the virus.
Especially remarkable is the fact that all known early SARS-CoV-2 genomes from humans (up to January 2020) vary by less than 30 bases. Conversely, the most closely related non-human
differ by over a thousand bases.
The importance of this is that “
Without a reliable root of the SARS‐CoV‐2 phylogeny, the most recent ancestor sequence cannot be accurately reconstructed, and it is not possible to assess the genetic diversity of SARS‐CoV‐2 that existed at the time of its first outbreak.”
Moreover, the distance of the Wuhan samples from the progenitor will remain unknown, as will the direction and order of the first mutations that gave rise to the various strains and lineages of SARS-CoV-2.
They used computational methods originally designed to find how mutations occurred within tumor cells in a single patient. The approach used is called a mutation order approach (MOA) and can provide a direct picture of the ancestral variants and mutations in order of time.
What were the findings?
MOA was employed on two sets of SARS‐CoV‐2 genomes, comprising almost 30,000 and 68,000 genomes, respectively, on two days three months apart. By tracing the mutational trail, inferred from the second genome set, they were able to understand how the virus is undergoing changes in different regions and at different times. They were able to track back to the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) of SARS-CoV-2.
Common ancestor
This progenitor viral genome has three bases that differ from the Wuhan strains. The researchers think that both the Wuhan and other of the earliest genomes to be sampled were actually variants of the progenitor coronavirus (CoV), which diverged into ν and α lineages.
Diversity pre-existing the earliest case
The Wuhan strain underwent three consecutive mutations, α1, α2, and α3, but these are not found in the closely related CoVs, all of which have the same base at these three positions. The ν variants of the progenitor CoV do not show the other 47 variants at these positions, making them unlikely to be the ancestral lineage for the Wuhan-1 virus or other early samples. The first ν mutant was picked up almost two months after the Wuhan-1 strain.
There were multiple occurrences of the progenitor CoV, both in China and the USA, from January 2020 onwards. Synonymous progenitor CoV samples were found in many other samples collected within two weeks of the Wuhan-1 strain.
While these were mostly Chinese and Asian (almost 90/130), they were found in all continents sampled and persisted up to April 2020 in Europe.
These findings suggest that the progenitor CoV was already spreading extensively before and after the first official reports of the emergence of a novel coronavirus in China. In other words, the Wuhan-1 strain is unlikely to be the original SARS-CoV-2 ancestor from which all currently circulating strains are derived.
This is in contrast to earlier studies, probably because this analysis uses more samples from a global database, and thus identifies the very early ν lineage, which is nonetheless not the MRCA. The latter is thought to have preceded the Wuhan variant by 6-8 weeks, that is, late October 2019.
In fact, Italian scientists found a
fragment from SARS-CoV-2 in Italy in early December, that exactly resembled the Wuhan-1 genome.
The analysis of the second set of genomes showed the same pattern leading to the same conclusions. Two new mutations were identified belonging to the ζ and η groups from the middle of March 2020.
Viral genomic fingerprints allow tracking over time and region
The mutational history led to a collection of genetic fingerprints extending from the progenitor CoV to the current strain. Each is named for the major variants included.
Both this progenitor genome and its branches have since led to an array of lineages or strains, some of which (e.g., D614G) have rapidly ascended to global or regional dominance in a very short time.
The North American strains have all belonged to the same lineages for the major part of the pandemic period. These were mostly αβ along with its mutant (αβγδ), which has remained dominant since April 2020.
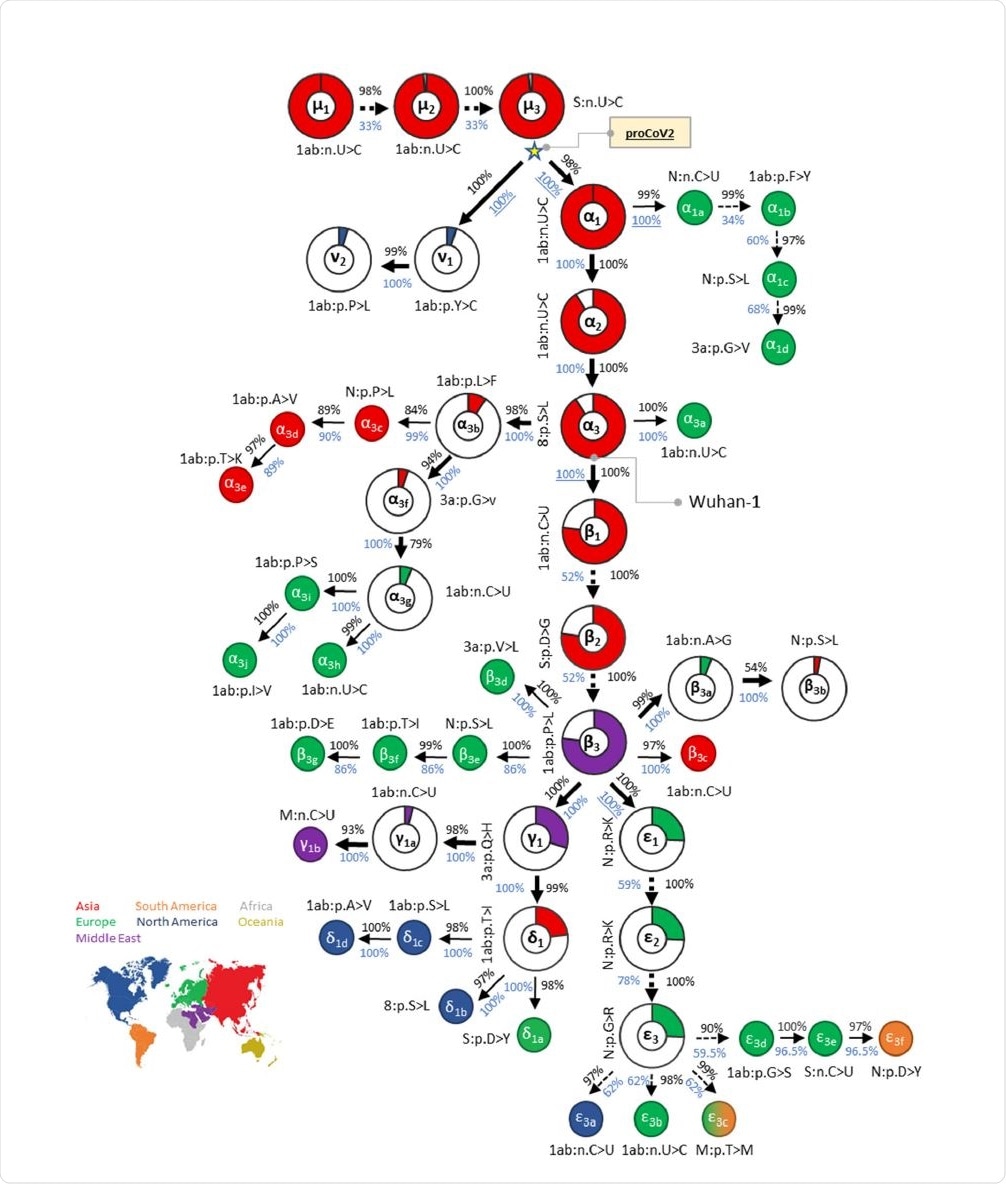
Mutational history graph of SARS-CoV-2 from the 29KG dataset. Thick arrows mark the pathway of widespread variants (frequency, vf = 3%), and thin arrows show paths leading to other common mutations (3% > vf > 1%). The pie-chart sizes are proportional to variant frequencies in the 29KG dataset, with pie-charts shown for variants with vf > 3% and pie color based on the world's region where that mutation was first observed. A circle is used for all other variants, with the filled color corresponding to the earliest sampling region. The co-occurrence index (COI, black font) and the bootstrap confidence level (BCL, blue font) of each mutation and its predecessor mutation are shown next to the arrow connecting them. Underlined BCL values mark variant pairs for which BCLs were estimated for groups of variants (see Materials and Methods) because of the episodic nature of variant accumulation within groups resulting in lower BCLs (<80%; dashed arrows). Base changes (n.) are shown for synonymous mutations, and amino acid changes (p.) are shown for nonsynonymous mutations along with the gene/protein names.
.jpg)
