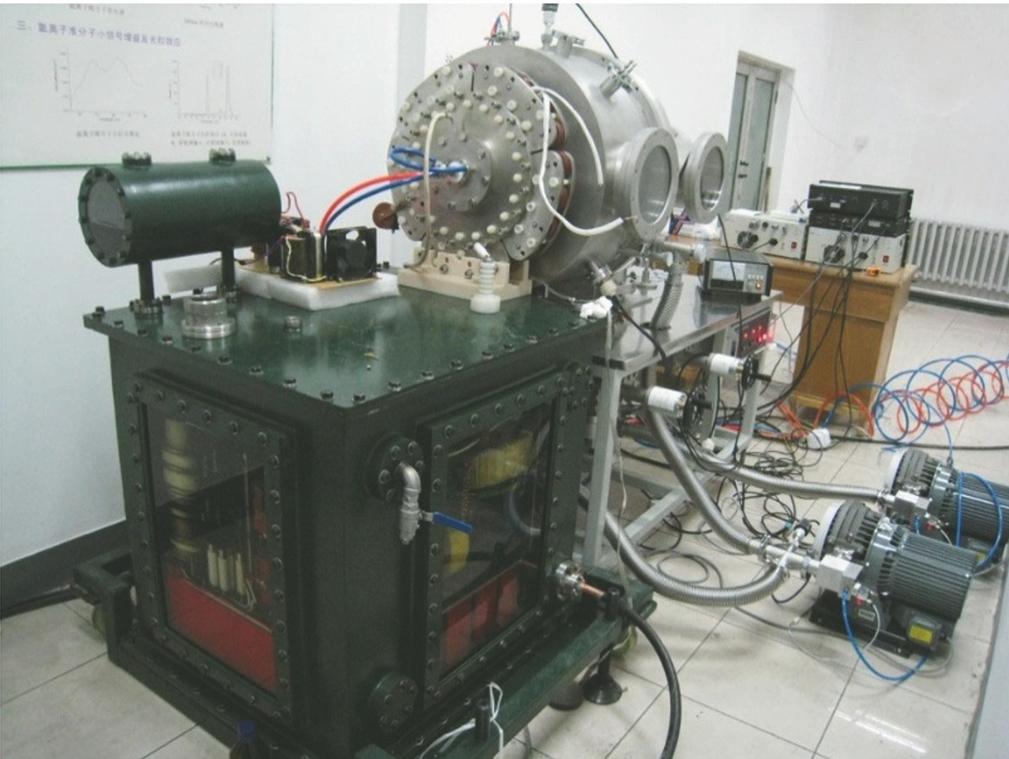
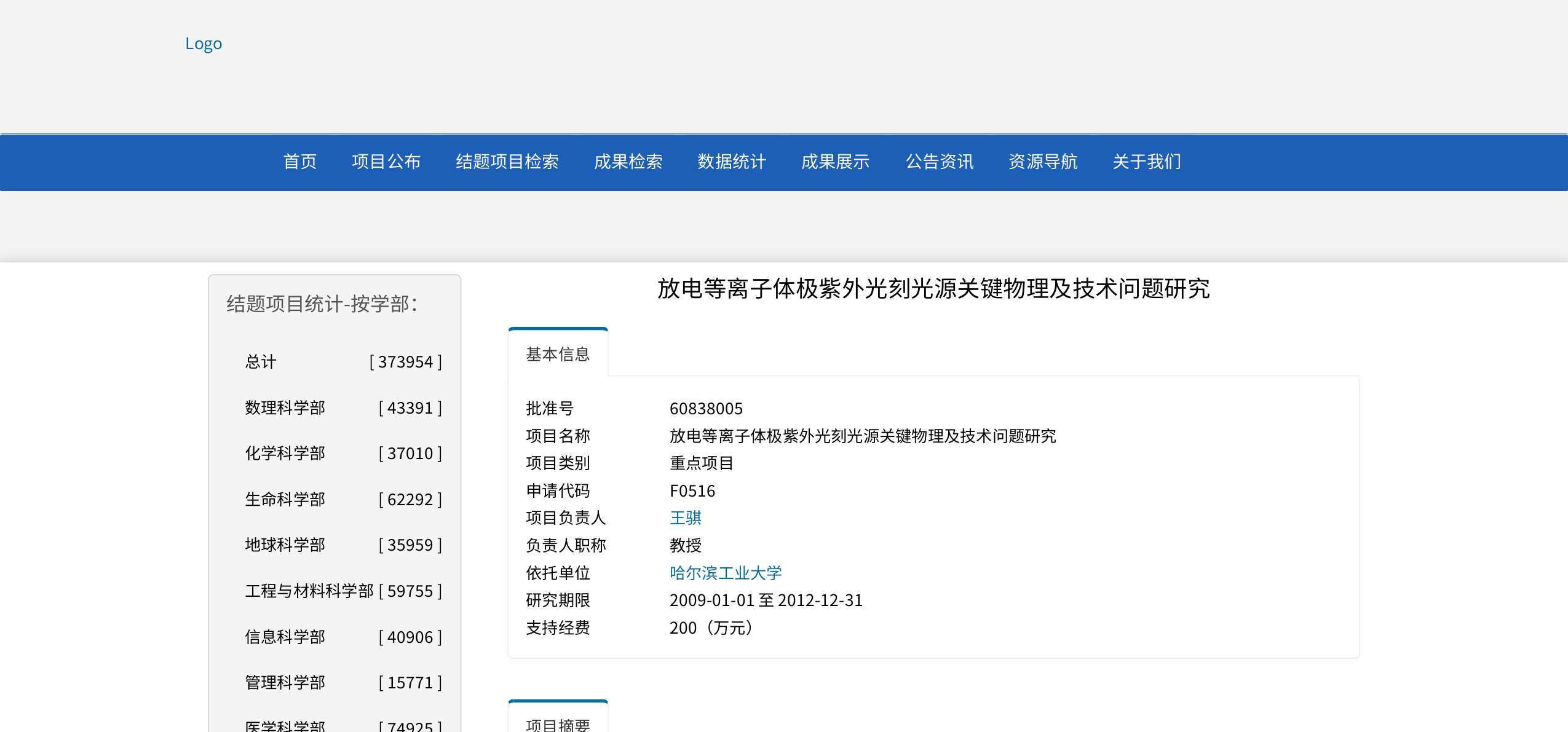
continue...
On the whole, in addition to some utility model patents, there are also a large number of withdrawn and terminated patent documents (Figure 6, Figure 7). Therefore , the number of effective invention patents is about 10 or so .
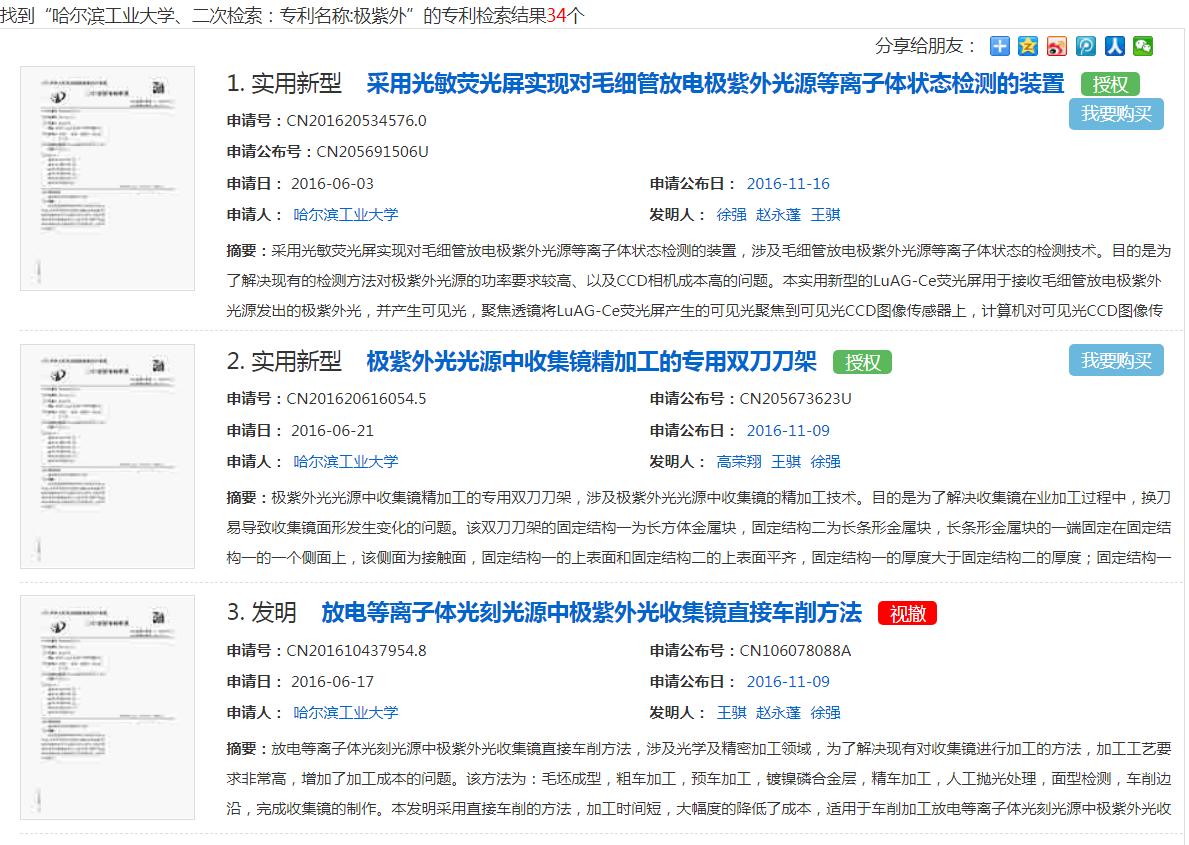
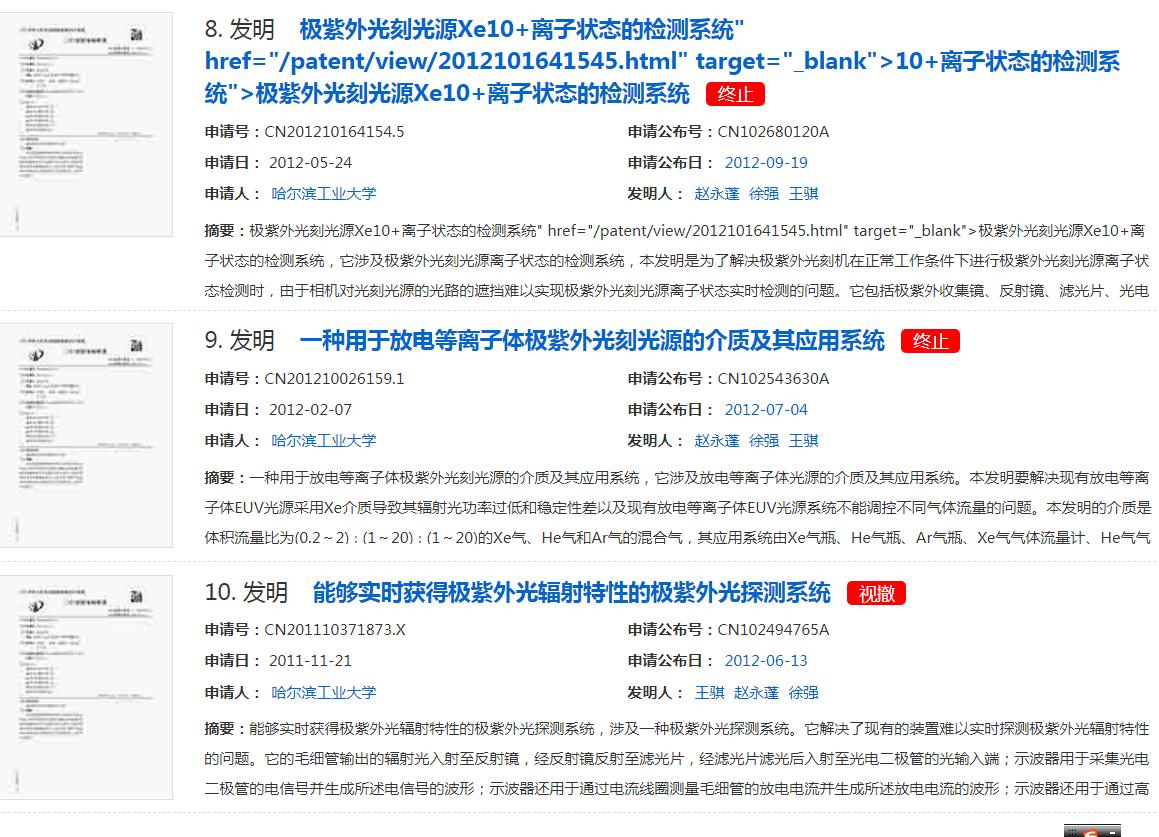
Some of the main invention patents are as follows:
2013-09-23:The finishing method of direct turning processing of the optical collecting mirror in the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2013-09-24:Invented the direct turning and rough machining method of the optical collecting mirror in the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2015-02-16:Invented the discharge chamber of the extreme ultraviolet light source for Xe dielectric capillary discharge detection
2016-05-31 : Invented a discharge electrode for capillary extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2016-06-17:Invented the base for the integration of the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source to collect the lens
2016-06-20:Invented a collection system for capillary discharge Z-pinch extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2016-06-22 : Invented a method for obtaining the circuit parameters of the magnetic pulse compression network in the power supply of the extreme ultraviolet light source
From the patent list, we can see that the EUV light source technology of Harbin Institute of Technology is actually based on the Xe gas capillary discharge technology , which is an early DPP light source technology.
It is worth mentioning that a 2016 patent " Inventing a discharge electrode for capillary extreme ultraviolet lithography light source " has been authorized by Heilongjiang Industrial Technology Research Institute (Figure 8). Whether this technology is used to manufacture DPP light sources is currently unknown.

The specific content of the EUV patent of Harbin Institute of Technology from 2000 to 2020
Since the English patent database contains some temporary patents, patent application documents, and patent documents, in order to more accurately analyze the content of the EUV patents of Harbin Institute of Technology, I focused on its 34 searchable patent documents in the Chinese patent database .On the whole, in addition to some utility model patents, there are also a large number of withdrawn and terminated patent documents (Figure 6, Figure 7). Therefore , the number of effective invention patents is about 10 or so .


Some of the main invention patents are as follows:
2013-09-23:The finishing method of direct turning processing of the optical collecting mirror in the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2013-09-24:Invented the direct turning and rough machining method of the optical collecting mirror in the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2015-02-16:Invented the discharge chamber of the extreme ultraviolet light source for Xe dielectric capillary discharge detection
2016-05-31 : Invented a discharge electrode for capillary extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2016-06-17:Invented the base for the integration of the extreme ultraviolet lithography light source to collect the lens
2016-06-20:Invented a collection system for capillary discharge Z-pinch extreme ultraviolet lithography light source
2016-06-22 : Invented a method for obtaining the circuit parameters of the magnetic pulse compression network in the power supply of the extreme ultraviolet light source
From the patent list, we can see that the EUV light source technology of Harbin Institute of Technology is actually based on the Xe gas capillary discharge technology , which is an early DPP light source technology.
It is worth mentioning that a 2016 patent " Inventing a discharge electrode for capillary extreme ultraviolet lithography light source " has been authorized by Heilongjiang Industrial Technology Research Institute (Figure 8). Whether this technology is used to manufacture DPP light sources is currently unknown.