He argues that the big fund gave 40% of the money to Unigroup/YMTC was a mistake,these kind of “shiny” project only works provided the US allow you to do so,since most money will end up in foreign equipment manufactures. He says big fund should distribute money to those critical parts of semiconductor supply chain,parts which are difficult to make profit in a very long time but critical to support the ecosystem.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Chinese semiconductor industry
- Thread starter Hendrik_2000
- Start date
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
Big fund is parallel to government support for the equipment side of the supply chain.He argues that the big fund gave 40% of the money to Unigroup/YMTC was a mistake,these kind of “shiny” project only works provided the US allow you to do so,since most money will end up in foreign equipment manufactures. He says big fund should distribute money to those critical parts of semiconductor supply chain,parts which are difficult to make profit in a very long time but critical to support the ecosystem.
I disagree. China needs to spend huge amounts of money on everything at the same time. Building more fabs with available tools, designing new products, making their own machine tools, etc. You cannot continue chasing the train. By the time you would get tools at the level of world level, the products you would design would be obsolete on arrival. And without people doing products how can you even evaluate the mass production qualities of the tools?
The nerf bat was going to hit sooner or later so the more technologies China can get into this window where it is still available the better.
The nerf bat was going to hit sooner or later so the more technologies China can get into this window where it is still available the better.
@olalavn Sir a follow up on your previous post regarding Huawei Litho patent.  From Huawei Central, Looking at this 2 with my previous post about Huawei 2016 patent below, we may see a working Huawei Lithographic machine next year, maybe the Mythical 22nm DUVL.
From Huawei Central, Looking at this 2 with my previous post about Huawei 2016 patent below, we may see a working Huawei Lithographic machine next year, maybe the Mythical 22nm DUVL.
Jul 22, 2020 — Huawei applied for patents on lithography equipment and systems four years ago ... Huawei is reportedly recruiting lithography process engineers, ...

Published
2 days ago
on
November 21, 2022
By
is continuously researching chipset printing technologies and the recent two patents suggest the research is making rapid progress. Adding to this, Huawei is also researching new patents for the extreme ultraviolet light of machines.
Therefore, Huawei is researching new technologies for chipset printing and manufacturing.
Let’s take a brief look at these patents.
ADVERTISEMENT
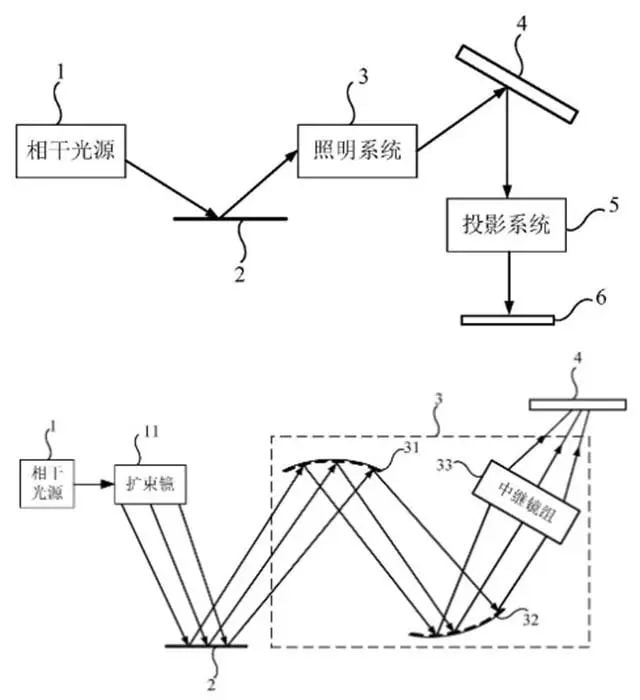
Details show a lithography device, and a control method thereof, which relate to the field of optics and can solve the problem that coherent light cannot be uniformed due to the formation of a fixed interference pattern.

The reflective surface of the reflective mirror includes a plurality of micro-reflective surfaces. The plurality of micro-reflecting surfaces includes a first micro-reflecting surface and a second micro-reflecting surface adjacent to the first micro-reflecting surface.
There is a height difference Ah between the first micro-reflecting surface and the second micro-reflecting surface, and the height difference Δh Located in the interval of (0, ka] where λ is the wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, while k is a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.
ADVERTISEMENT
The patent shows a lithography device, which makes the accumulated light intensity of the illumination field of view uniform during the exposure time by continuously changing the interference pattern formed by coherent light.
This will the device to achieve the purpose of uniform light. It also solves the problem in the related art that the light cannot be uniformed due to the coherent light forming a fixed interference pattern.
It can be observed that Huawei has been researching to solve the chip neck problem for lithography machines because it’s an essential part of breakthroughs for chipset development.
ADVERTISEMENT
Hence, it’s possible that Huawei could achieve a 100% Chinese chipset printing machine in the near future.
Jul 22, 2020 — Huawei applied for patents on lithography equipment and systems four years ago ... Huawei is reportedly recruiting lithography process engineers, ...
Huawei is rapidly researching on chipset printing technologies

Published
2 days ago
on
November 21, 2022
By

is continuously researching chipset printing technologies and the recent two patents suggest the research is making rapid progress. Adding to this, Huawei is also researching new patents for the extreme ultraviolet light of machines.
Lithography:
Lithography technology is the most critical step in chipset manufacturing. The reason why chip technology has been able to develop gradually from 100 microns to 3nm in the past 60 years is due to lithography machines. Without a lithography machine, there’s no chipset manufacturing.Therefore, Huawei is researching new technologies for chipset printing and manufacturing.
Let’s take a brief look at these patents.
ADVERTISEMENT
First patent:
A patent was filed on May 13, 2021, have now been published. The technical details of this patent cover the related technologies of extreme ultraviolet light.Details show a lithography device, and a control method thereof, which relate to the field of optics and can solve the problem that coherent light cannot be uniformed due to the formation of a fixed interference pattern.

The reflective surface of the reflective mirror includes a plurality of micro-reflective surfaces. The plurality of micro-reflecting surfaces includes a first micro-reflecting surface and a second micro-reflecting surface adjacent to the first micro-reflecting surface.
There is a height difference Ah between the first micro-reflecting surface and the second micro-reflecting surface, and the height difference Δh Located in the interval of (0, ka] where λ is the wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, while k is a positive integer greater than or equal to 1.
ADVERTISEMENT
Second patent:
The second patent is titled “Mirror, Photolithography Device and Control Method”. It has a patent application number of CN202110524685.X. This can solve the problem that coherent light cannot be homogenized due to the formation of a fixed interference pattern, which is also a common problem in EUV lithography.The patent shows a lithography device, which makes the accumulated light intensity of the illumination field of view uniform during the exposure time by continuously changing the interference pattern formed by coherent light.
This will the device to achieve the purpose of uniform light. It also solves the problem in the related art that the light cannot be uniformed due to the coherent light forming a fixed interference pattern.
It can be observed that Huawei has been researching to solve the chip neck problem for lithography machines because it’s an essential part of breakthroughs for chipset development.
ADVERTISEMENT

Outcome:
It seems that Huawei is pushing itself to the limits in the field of lithography machines. Meanwhile, the lithography technology shows that Huawei will make a breakthrough, combined with other companies in the future.Hence, it’s possible that Huawei could achieve a 100% Chinese chipset printing machine in the near future.
he is wrong. without YMTC then there's low demand for the domestic equipment. SMIC cannot supply that demand, as it is a listed private company, while YMTC can, since it is state owned.He argues that the big fund gave 40% of the money to Unigroup/YMTC was a mistake,these kind of “shiny” project only works provided the US allow you to do so,since most money will end up in foreign equipment manufactures. He says big fund should distribute money to those critical parts of semiconductor supply chain,parts which are difficult to make profit in a very long time but critical to support the ecosystem.
In almost every product, you don't start out with high quality components, then build equipment from high quality components. It is always first make a finished product with low quality or imported components, then localize and increase quality from there.
Example, the first steam engine didn't have superalloy turbine blades, it was hand made with a primitive iron piston. But the makers of steam engines eventually demanded higher and higher quality from the component suppliers, and now you have high tech steam turbines with superalloy single crystal blades.
Jiangfeng Electronics and Qinchuan Machine Tool signed a contract for the "Collaborative Innovation Center for High-end Equipment of Ultra-high-purity Metal Sputtering Targets for Integrated Circuit Manufacturing"
on November 21, Ningbo Jiangfeng Electronic Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Jiangfeng Electronics") signed a contract with Qinchuan Machine Tool Group to jointly build a "high-end ultra-high-purity metal sputtering target for integrated circuit manufacturing" Equipment Collaborative Innovation Center".
Jiangfeng Electronics reported that through the establishment of "Qinchuan Machine Tool-Jiangfeng Electronics Semiconductor Target High-end Equipment Innovation Center", it will carry out basic theory and core technology research, collaborative innovation base construction, collaborative innovation team building, and innovative talent training. , Accelerate the breakthrough of high-end manufacturing technology of target equipment technology.
on November 21, Ningbo Jiangfeng Electronic Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as "Jiangfeng Electronics") signed a contract with Qinchuan Machine Tool Group to jointly build a "high-end ultra-high-purity metal sputtering target for integrated circuit manufacturing" Equipment Collaborative Innovation Center".
Jiangfeng Electronics reported that through the establishment of "Qinchuan Machine Tool-Jiangfeng Electronics Semiconductor Target High-end Equipment Innovation Center", it will carry out basic theory and core technology research, collaborative innovation base construction, collaborative innovation team building, and innovative talent training. , Accelerate the breakthrough of high-end manufacturing technology of target equipment technology.
Comparing CN's semicon project (litho,Eda,etching,chemicals etc) to CN's other Major projects:
Atomic project: 1,000 scientists & technicians
Space projects (manned, tiangong,beidou,moon,mars etc)
CASC with over 200,000 ppl
Huawei, 200,000 ppl
with revenue of abt $300 millions per day!
BYD 300,000 ppl
CATL 35,000 ppl
do you think SMEE AMEC etc have a snowball's chance in hell?
Atomic project: 1,000 scientists & technicians
Space projects (manned, tiangong,beidou,moon,mars etc)
CASC with over 200,000 ppl
Huawei, 200,000 ppl
with revenue of abt $300 millions per day!
BYD 300,000 ppl
CATL 35,000 ppl
do you think SMEE AMEC etc have a snowball's chance in hell?
Do you get medical advices from your masseuse? The guy and his team are civil engineers.He argues that the big fund gave 40% of the money to Unigroup/YMTC was a mistake,these kind of “shiny” project only works provided the US allow you to do so,since most money will end up in foreign equipment manufactures. He says big fund should distribute money to those critical parts of semiconductor supply chain,parts which are difficult to make profit in a very long time but critical to support the ecosystem.
Bro you forget the most important Institution.Comparing CN's semicon project (litho,Eda,etching,chemicals etc) to CN's other Major projects:
Atomic project: 1,000 scientists & technicians
Space projects (manned, tiangong,beidou,moon,mars etc)
CASC with over 200,000 ppl
Huawei, 200,000 ppl
with revenue of abt $300 millions per day!
BYD 300,000 ppl
CATL 35,000 ppl
do you think SMEE AMEC etc have a snowball's chance in hell?
The Chinese Academy of Science or CAS.
Research strength
CAS scientists conduct research in most areas of basic science and technology as well as strategic advanced technologies and areas related to the public welfare and the development of emerging industries. CAS comprises 104 research institutes, 12 branch academies, three universities and 11 supporting organizations in 23 provincial-level areas throughout the country. These institutions are home to more than 100 national key labs and engineering centres as well as nearly 200 CAS key labs and engineering centres. Altogether, CAS comprises 1,000 sites and stations across the country.

CAS is home to over 80 percent of China’s large-scale science facilities. Eleven of them are currently in operation, including the Beijing Electron Positron Collider (BEPCII), the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokomak (EAST), the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), and the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST), among others. CAS is also developing the China Spallation Neutron Source (CSNS) and the 500-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), as well as other facilities.
The academy also hosts the Chinese Ecosystem Research Network (CERN), which has about 50 core field stations and 100 other stations across the country. CERN conducts monitoring and research involving ecological systems and the environment.
CAS is also home to 13 botanical gardens and 26 herbaria, as well as a 150-TB scientific data storage facility. Environmental research is one of CAS’s traditional strengths.
In addition, CAS publishes 267 academic journals.
CAS has a staff of 67,900, including about 56,000 professional researchers. Of these, approximately 22,800 are research professors or associate professors. By 2020, CAS hopes to have a few thousand leading scientists working for the organization. It has long been a CAS strategy to emphasize the combination of research and education and interdisciplinary and cross-sector cooperation in innovation.
Academy scientists now implement about 30 percent of China’s Key Basic Science Projects under the nation’s 973 Program. In addition, CAS researchers have won 19 first-class National Natural Sciences Prizes of the 32 awarded. Also, 34.2 percent of all researchers named as National Excellent Young Scholars are affiliated with CAS. Furthermore, 40 percent of the principle investigators for key natural science projects funded under the National Natural Science Foundation of China are affiliated with CAS.
CAS’s most recent achievements include a series of breakthroughs in quantum communication and computing, new progress in the study of re-emerging superconductivity, major breakthroughs in stem cell research and the discovery of a key factor in regulating the development of brain intelligence.
Emphasis on talent
Cultivating, recognizing and deploying talent is a key feature of CAS — accomplished through CAS’s roles as an educational institution and academic society.

CAS nurtures young S&T talent through three affiliated universities, the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS) and ShanghaiTech University. So far, CAS has graduated 85,884 masters and 64,977 PhDs.
UCAS, located in Beijing, has a total enrollment of 41,216 students, most of which are doctoral candidates. Its predecessor was the Graduate School of CAS. Since 2014, UCAS started to recruit 300+ undergraduates. One unique feature of UCAS is its dual-phrase education on the integration of education and research with graduates taking the course-work at the university and doing research training and dissertation at the institutes.
USTC, based in Hefei, Anhui Province, has a total enrollment of 17,800 students, including about 10,000 graduates. Established in Beijing in 1958 and moved to Hefei in 1970, USTC enjoys excellent reputation worldwide. The strategy that CAS adopts in running the university is to get the whole Academy involved in its education and to combine research institutes with departments and schools of the university.
ShanghaiTech, being rapidly built, is a partnership university between CAS and the Shanghai Municipal Government. It focuses on science and engineering.
CAS membership is the highest academic accolade in the field of science and technology in China. Membership is a lifelong honor conferred by the presidium of CAS, based on a rigorous and limited biennial election process. The three types of Members — Full, Emeritus and Foreign — are grouped into six academic divisions: Mathematics and Physics; Chemistry; Biological and Medical Sciences; Earth Sciences; Information Technology Sciences; and Technological Sciences. These divisions function as a national scientific think tank in partnership with the whole academy. Members provide advice to the government and society on major issues concerning China’s economy, social development and S&T progress. In addition, they provide guidance on the development of individual scientific disciplines and on the development of the academy itself. Furthermore, they promote public understanding of science and technology through public lectures and domestic and international cooperation. Currently, there are 777 Full and Emeritus Members, as well as 82 Foreign Members. Fifteen CAS Members have received China’s highest national science award — of 20 total recipients.
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
