You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
China's Space Program Thread II
- Thread starter Blitzo
- Start date
by78
General
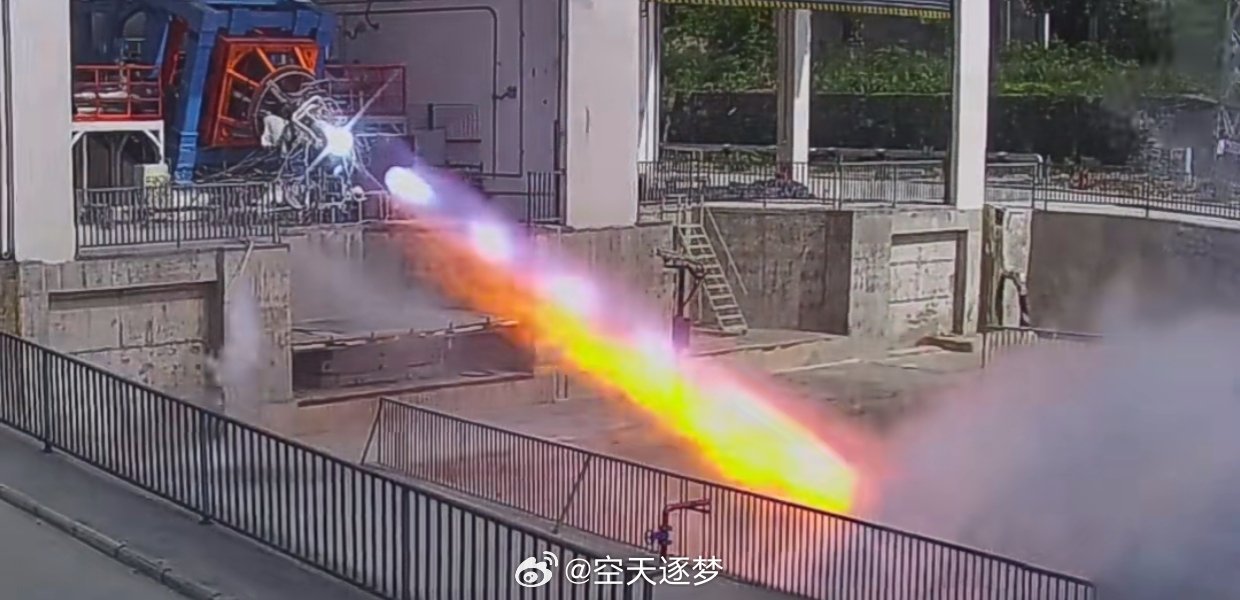
An update on the 70-ton reusable LOX/Methane Mingfeng-2 engine being developed by ExSpace. In the past year, prototypes have undergone extensive hot test runs of various durations and scenarios, including multiple restarts and variable thrust, and performance has met all design parameters.
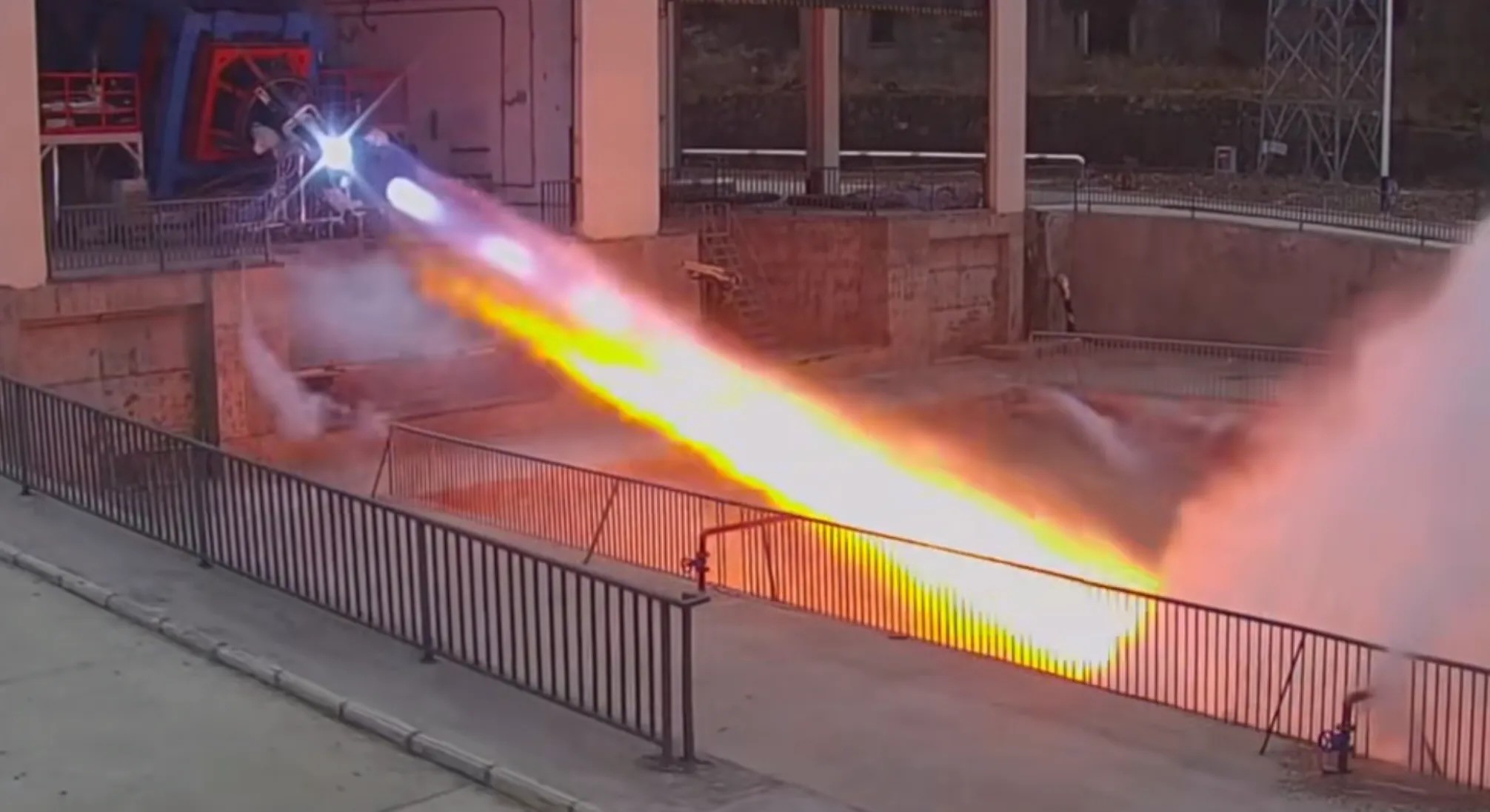

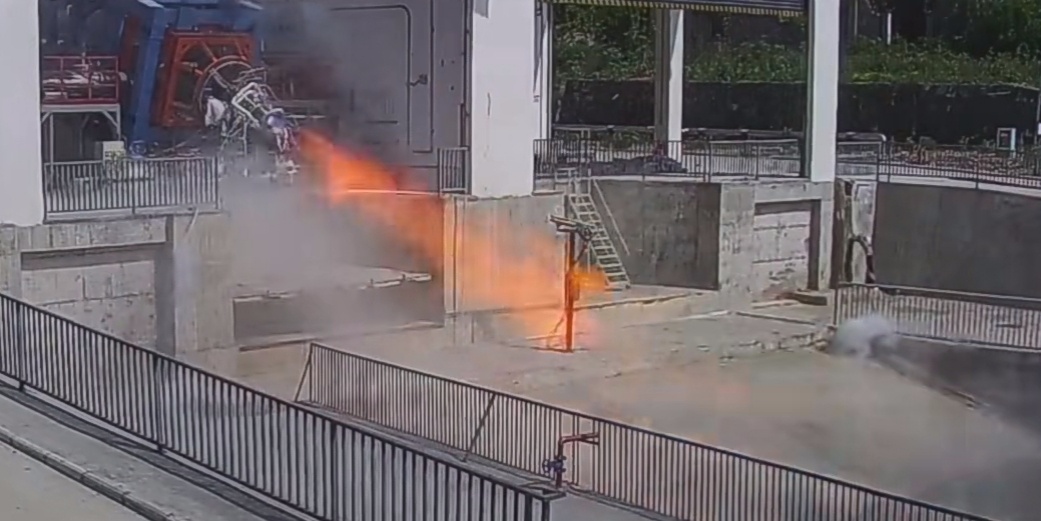
Tests on the 70-ton reusable LOX/Methane Mingfeng-2 engine continues. The engine recently completed an hour-long hot test run, during which multiple ignitions were successfully carried out.


by78
General
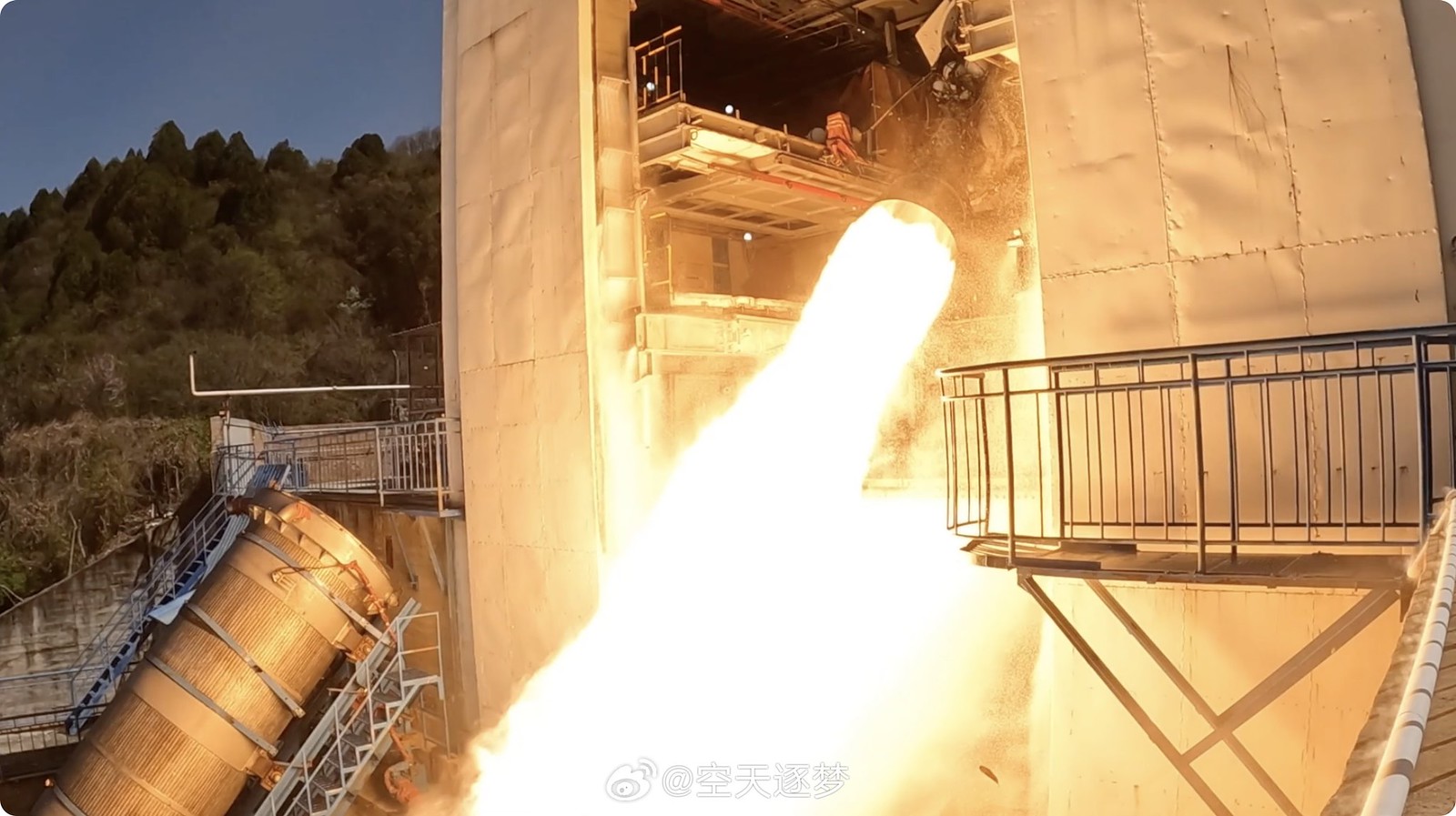
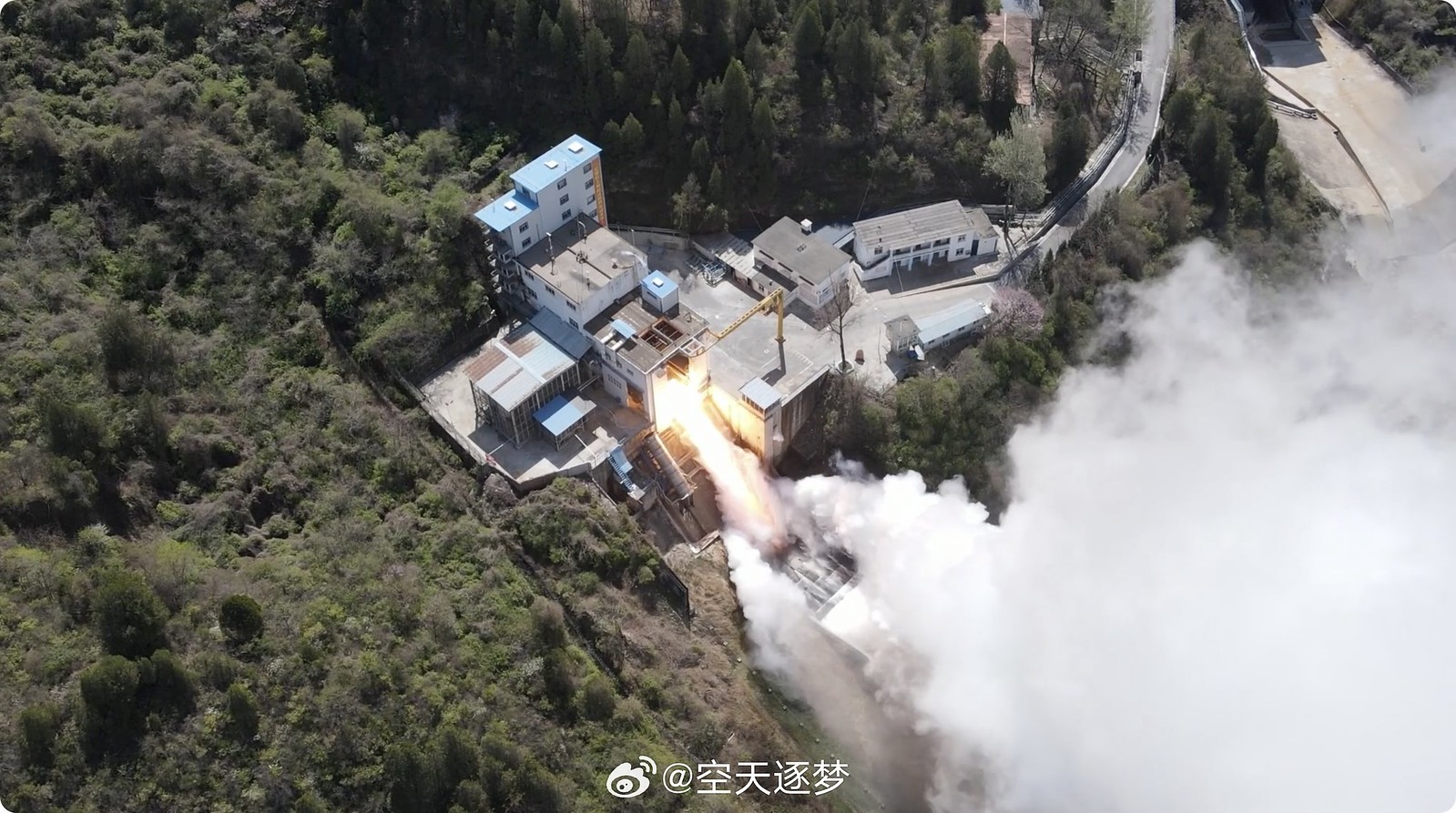
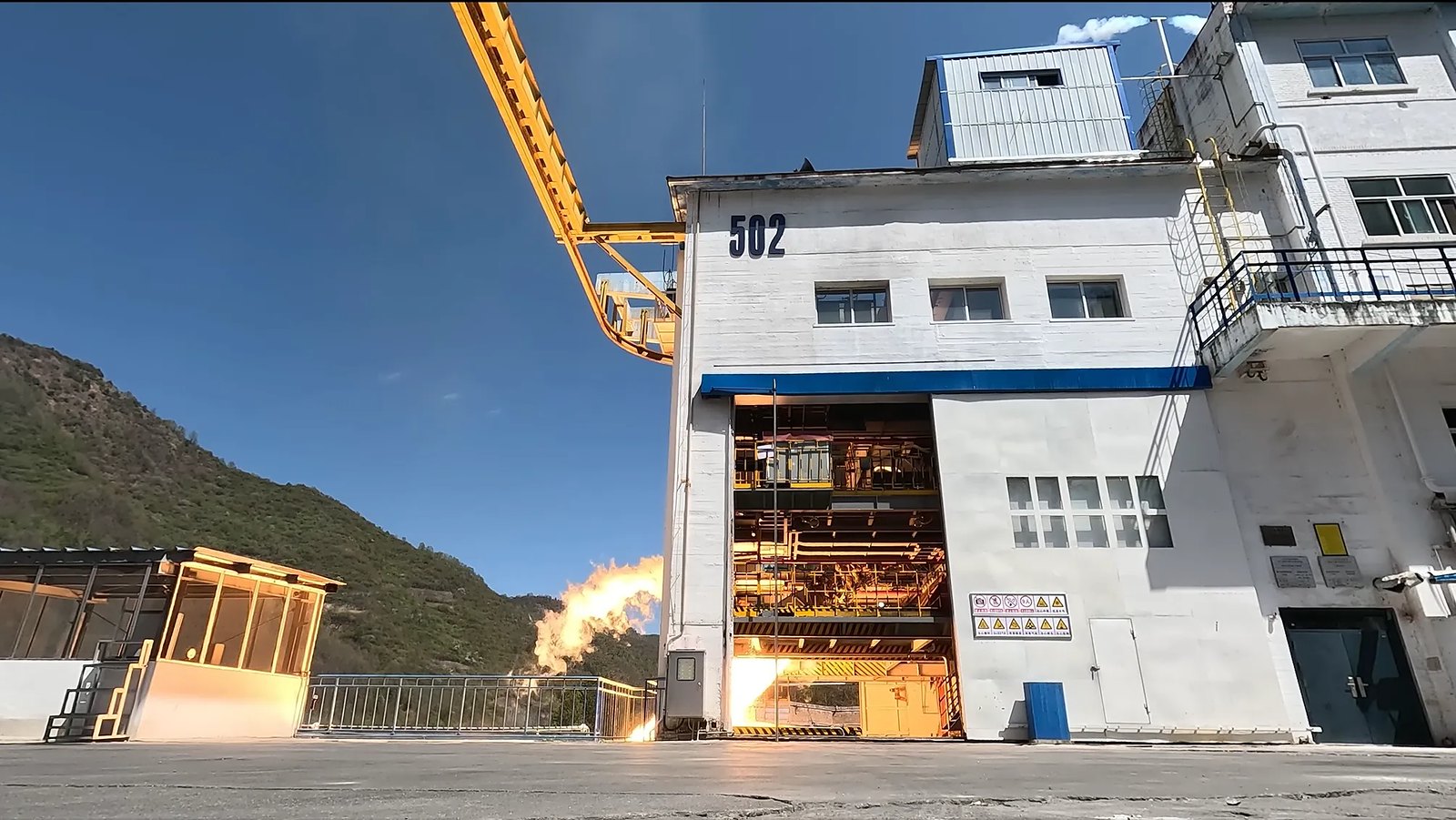
An article on the development progress of the reusable 130-ton YF-100N engine intended for the first stage of Long March 10. Basically, the project is coming along along, with various components and technologies having been repeatedly tested, as well as hot test runs carried out, all of which demonstrated the feasibility of the YF-100N design and verified its mission profile.

An update on the 130-ton YF-100N LOX/Kerosene reusable engine. The engine has accumulated more than 3900 seconds in hot test runs, during which it completed 30 ignitions (15 restarts).




by78
General
The Honghu satellites launched on December 9th featured Hall thrusters using krypton propellant. The thrusters were successful ignited at 6:49AM on December 26, Beijing Time, marking the first time that China has achieved on-orbit operation of Hall thrusters using Krypton propellant. The Hall thrusters (Model SW-200) were developed by Hongqing Technology (鸿擎科技).

As of April 24, SW-200 krypton Hall thrusters have accumulated a total ignition time of 172.92 hours, with 361 on-orbit ignitions. This is the first time China has achieved (100km-level) orbit control using krypton Hall electric propulsion.


by78
General
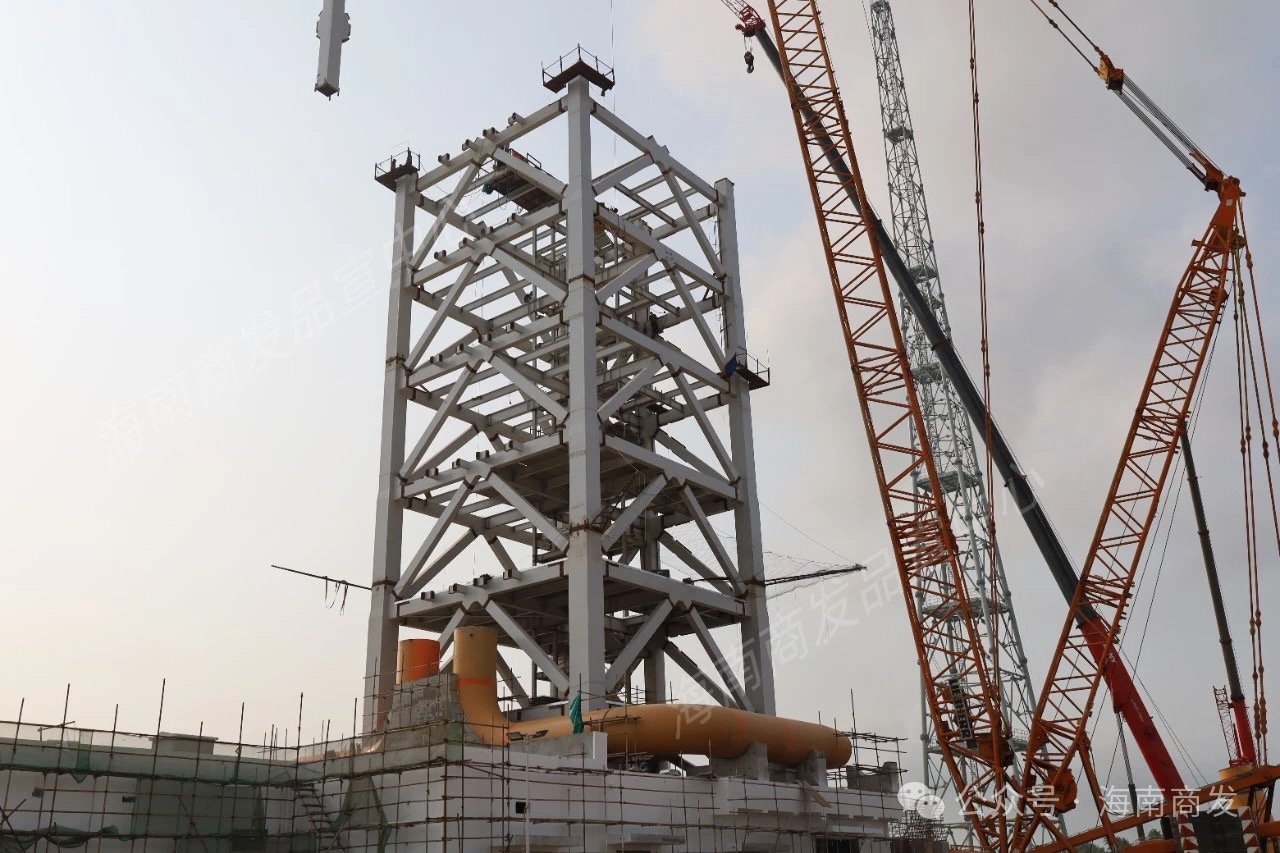
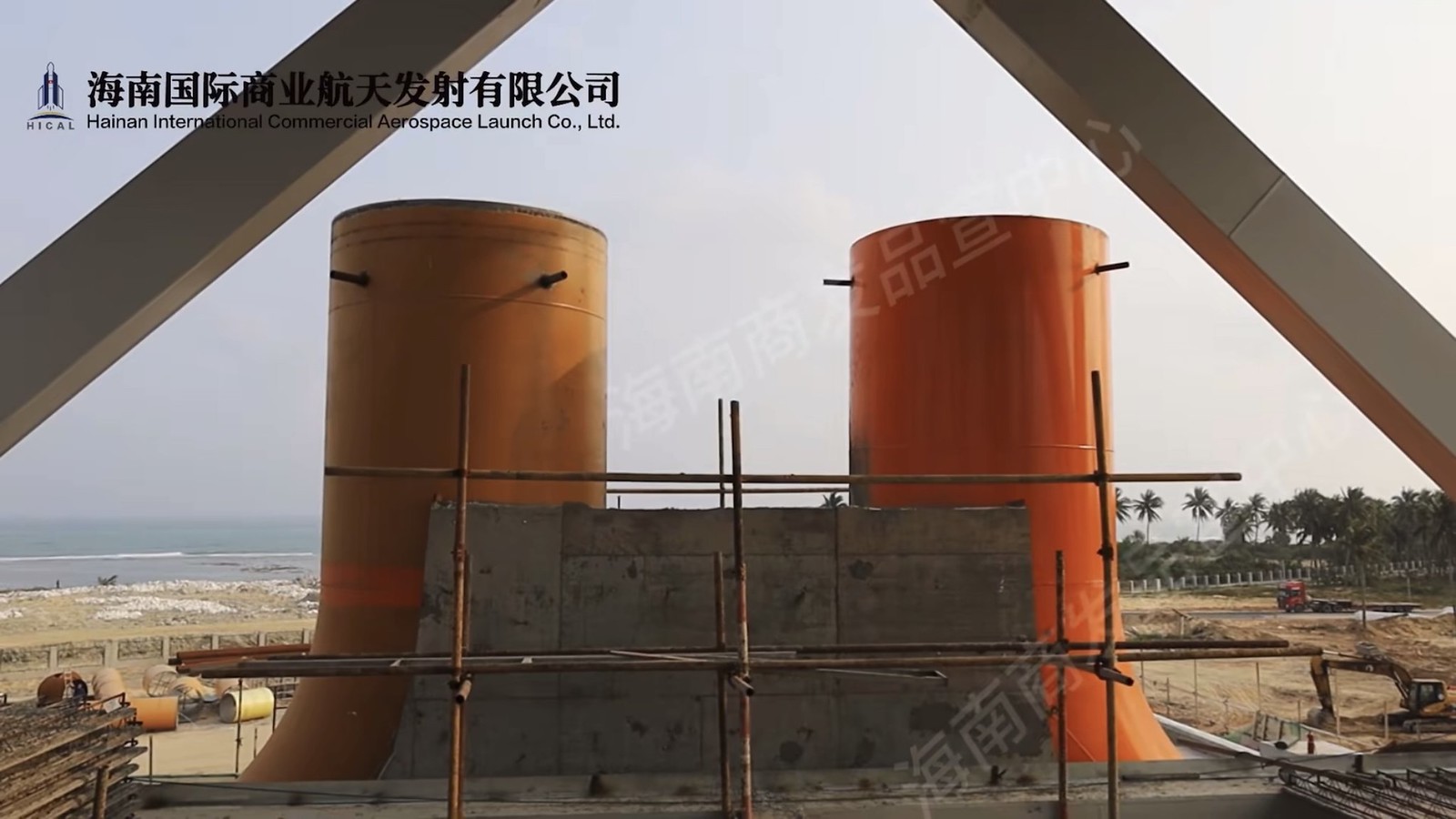
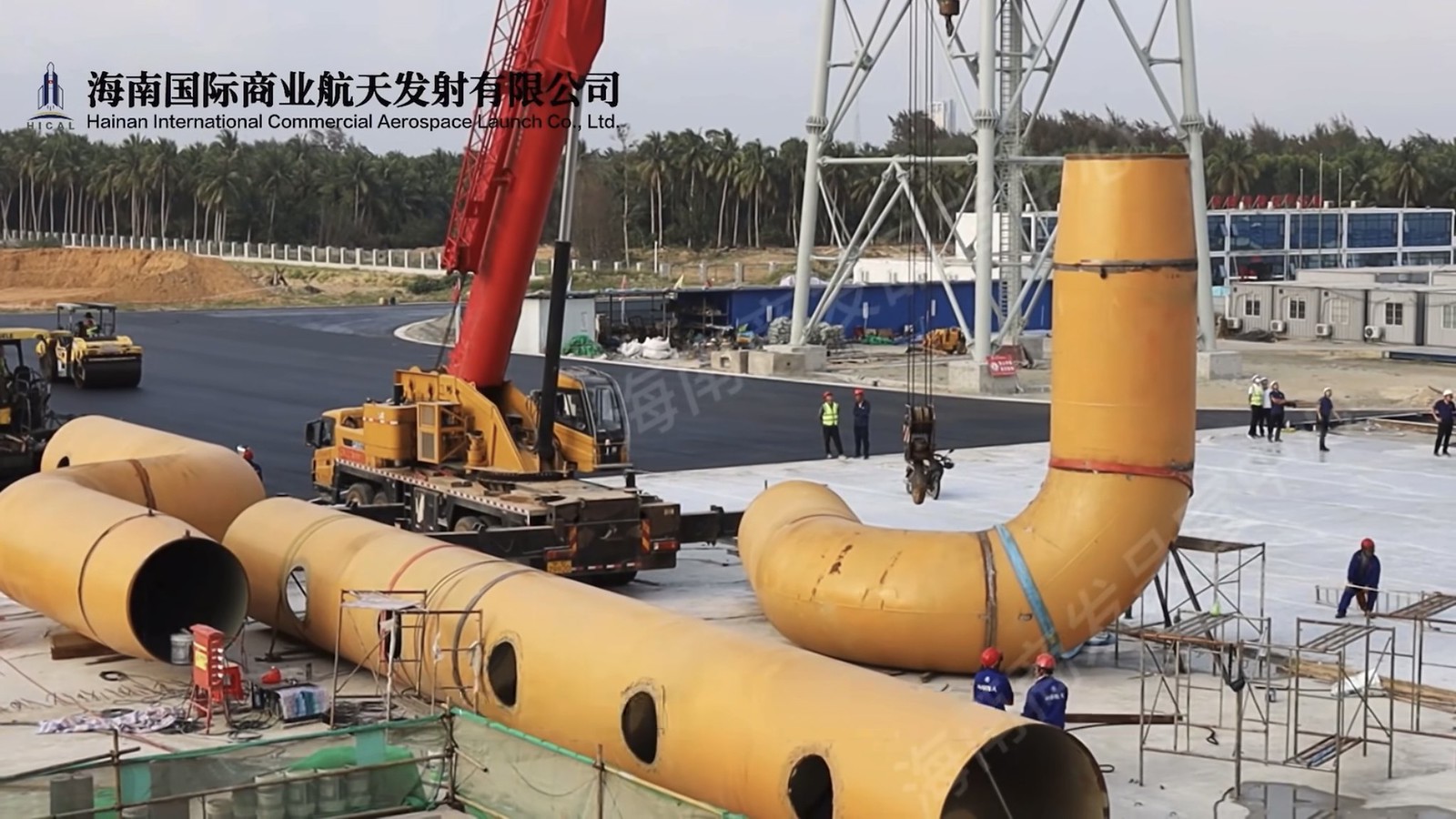
The Chairman of Galactic Energy revealed in an interview that his company plans to build a rocket testing facility in Wenchang to inspect and maintain recovered reusable rockets and to prepare them for their next flights.

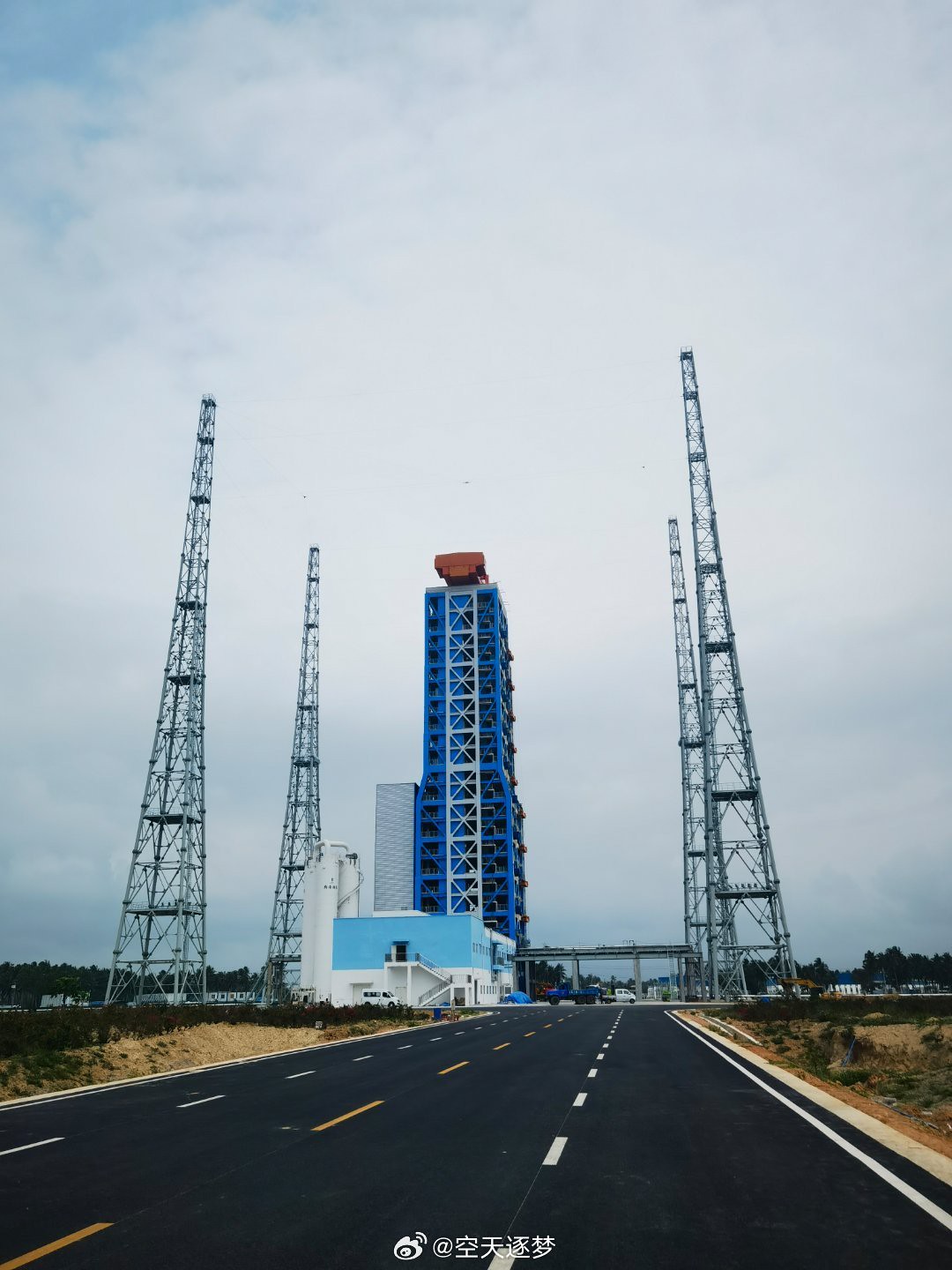
In a sign that private launch providers are quickly coalescing their infrastructure around Wenchang, i-Space/Interstellar Glory also announced that it plans to build a rocket assembly and testing facility in Wenchang, which will have the capacity to inspect and recycle 40 recovered reusable rockets annually.

More slides from i-Space/Interstellar Glory, with salient points being summarized below:
1) Infrastructure construction:
– The Pangezhuang launch vehicle production base in Daxing District, Beijing houses various facilities for rocket assembly and testing, propellant tank (stir-welding) production, LOX/Methane engine mass production, attitude and orbital control units final assembly, and liquid launch vehicle R&D, etc. The Pangezhuang base has achieved trial production capacity.
– The propellant tank welding production line has completed equipment debugging and process verification. i-Space is currently developing a 4.2-meter propellant tanks.
– A high-thrust engine test bench and a power system test bench are under construction.
– The company is actively participating in the construction of commercial launch sites, as well as building a facility for recycling recovered rockets.
2) Launch vehicle lineup:
– SQX-1 small solid-fueled vehicle
– SQX-2Y reusable technology verification vehicle
– SQX-2 small reusable vehicle
– SQX-3, and -3B medium-and-large reusable vehicle
3) R&D on reusable launch technology:
– Through the development of SQX-2/2Y, 18 key technical breakthroughs have been made, which were verified through simulation and/or ground tests, and the vertical takeoff and landing demonstration was successfully carried out twice (on November 2 and December 10, 2023, respectively).
– For the development of SXQ-3, focus is placed on six key technical areas: overall design of reusable launch vehicles, high thrust-to-mass-ratio 100-ton LOX/Methane engine, design and manufacturing of large-diameter tank frame-and-truss reinforced barrel sections, non-pyrotechnic stage separation, intelligent fault diagnosis and analysis, engine containment in case of RUD, etc. The rocket has completed a total of 45 verification tests, fully verifying key reusability technologies.
4) First orbital test flight of SQX-3 will be conducted in 2025 and first orbital flight with recovery will be carried out in 2026. By 2030, i-Space plans to have an annual launch capacity of 20 per year, basically achieving cost-effective, efficient, and volume launch capability.


Last edited: