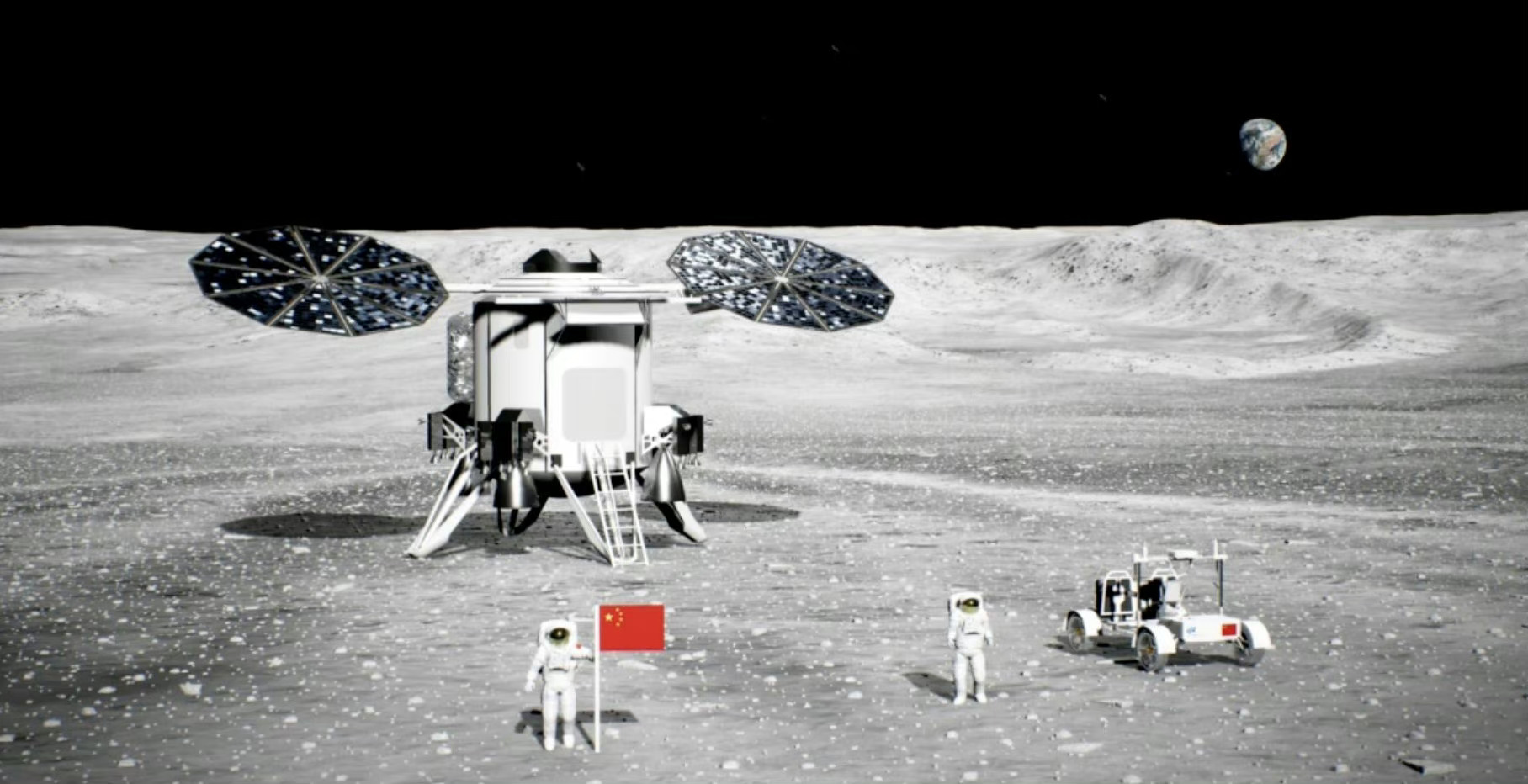
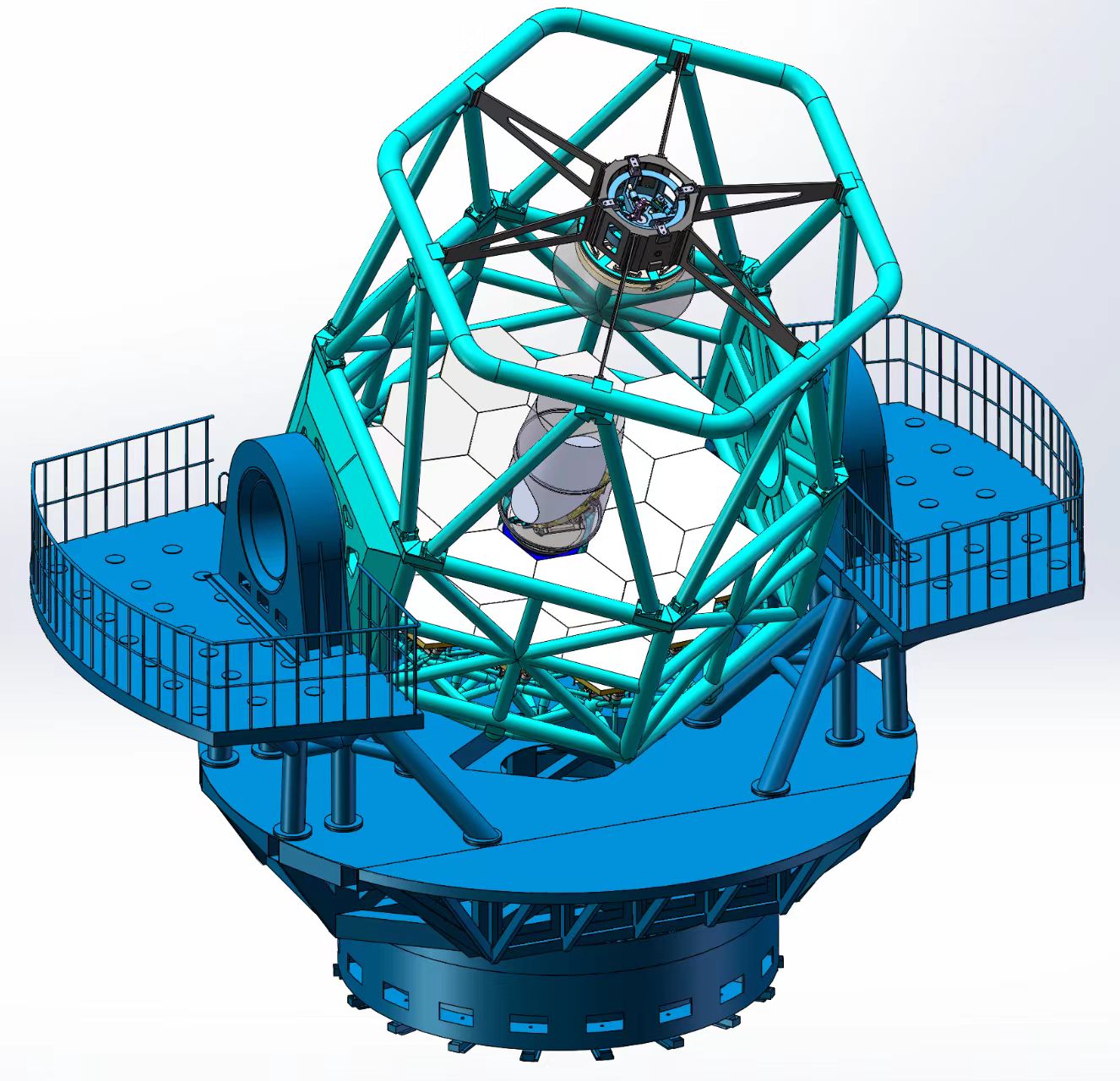
China eyes building its most powerful spectroscopic telescope, the Jiaotong University Spectroscopic Telescope (JUST), at NW China's Lenghu astronomical observation base. Set to start service by 2026, the 4.4-m caliber JUST will have a primary mirror with 18 hexagonal sub-mirrors..
AIMS telescope has used an ultra-narrowband Fourier spectrometer to achieve the expected goal of directly measuring the Zeeman split distance to obtain the intensity of the solar magnetic field in the mid-infrared band, breaking through the bottleneck problem in the measurement of the solar magnetic field in the century-old history, and realizing the change of the solar magnetic field from ' The leap from indirect measurement to direct measurement." Wang Dongguang said, "The Zeeman split distance is proportional to the square of the wavelength. Before the AIMS telescope, the solar magnetic field was mostly observed in the visible light or near-infrared band. Since the split distance is very small, the observation It is difficult for instruments to distinguish. The operating wavelength of the AIMS telescope is 12.3 microns. Under the same magnetic field strength, the Zeeman split distance increases hundreds of times, making 'direct measurement' possible."
The AIMS telescope is the world's first equipment dedicated to mid-infrared solar magnetic field observation, and will reveal the mystery of the sun in the mid-infrared band.
"By eliminating stray light optical design and vacuum refrigeration and other technologies, we have solved the problems faced by infrared solar observations in this band such as high environmental background noise and reduced detector performance." Feng Zhiwei, a senior engineer at the National Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said that the infrared imaging terminal is made of infrared It consists of three systems: optics, focal plane array detector and vacuum refrigeration. All components including the detector chip are made in China. This terminal system is mainly used for solar monochromatic imaging observations in the 8 to 10 micron band to study the material and energy transfer mechanism during the violent explosion of the sun.