You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
News on China's scientific and technological development.
- Thread starter Quickie
- Start date
Equation
Lieutenant General
And it smells in ALL of them. The Bay Area Rapid Transit was pretty good. The best subway I've been to in North America so far is in Montreal, Canada.New York subway have something similiar. Except cars either have AC on full blast or not all. And also whether or not a car has AC is randomized, you don't know which car has what until after you get on. At which point it becomes difficult in practice to get off and try another car.
Jura The idiot
General
now noticed the tweet
The coastal city of Qingdao, Shandong Province has become the 1st city in China to offer network coverage on city bus lines
now
·
Shaolin Temple has entered the era! Seven stations have started operatiing in the C China's Henan-based scenic spot known around the world for Chinese and martial arts.
The coastal city of Qingdao, Shandong Province has become the 1st city in China to offer network coverage on city bus lines
now
·
Shaolin Temple has entered the era! Seven stations have started operatiing in the C China's Henan-based scenic spot known around the world for Chinese and martial arts.
solarz
Brigadier
And it smells in ALL of them. The Bay Area Rapid Transit was pretty good. The best subway I've been to in North America so far is in Montreal, Canada.
I grew up in Montreal, loved the subway there.
Have you been on any Chinese subways? The Shanghai and Beijing subways are easily the best in the world.
When I went to Europe, I found the Parisian subway to be also pretty old and dirty, but the Barcelona subway was new and clean, and looked a lot like the Shanghai subways.
As a frequent user of BART good isn’t the word I would use.And it smells in ALL of them. The Bay Area Rapid Transit was pretty good. The best subway I've been to in North America so far is in Montreal, Canada.
Montreal has an underrated metro system. Spent part of my childhood there.I grew up in Montreal, loved the subway there.
Have you been on any Chinese subways? The Shanghai and Beijing subways are easily the best in the world.
When I went to Europe, I found the Parisian subway to be also pretty old and dirty, but the Barcelona subway was new and clean, and looked a lot like the Shanghai subways.
Equation
Lieutenant General
I grew up in Montreal, loved the subway there.
Have you been on any Chinese subways? The Shanghai and Beijing subways are easily the best in the world.
When I went to Europe, I found the Parisian subway to be also pretty old and dirty, but the Barcelona subway was new and clean, and looked a lot like the Shanghai subways.
Not yet, but one day I sure will.
Jura The idiot
General
now noticed the tweet
NW China’s Qinghai province has launched a power supply project to offer electricity fully by clean energy for 15 consecutive days. Starting from June 9, the project is to set a new world record for entire clean energy supply.
NW China’s Qinghai province has launched a power supply project to offer electricity fully by clean energy for 15 consecutive days. Starting from June 9, the project is to set a new world record for entire clean energy supply.
Jura The idiot
General
now
·
China's spacecraft tracking ship Yuanwang-3 successfully arrived in the southern Pacific Ocean on Thursday. Crew members started to carry out overall examinations and tests of the facilities for upcoming satellite maritime monitoring missions.
***
the Southern Pacific Ocean is as far as it gets from here; if I had gone right through the Earth, I would've emerged off
LOL
·
China's spacecraft tracking ship Yuanwang-3 successfully arrived in the southern Pacific Ocean on Thursday. Crew members started to carry out overall examinations and tests of the facilities for upcoming satellite maritime monitoring missions.
***
the Southern Pacific Ocean is as far as it gets from here; if I had gone right through the Earth, I would've emerged off
LOL
Jura The idiot
General
only now I read this
Interview: Supercomputing to fuel innovation for industries, serve daily routines: Chinese scientist
Xinhua| 2019-06-19 10:08:25
Interview: Supercomputing to fuel innovation for industries, serve daily routines: Chinese scientist
Xinhua| 2019-06-19 10:08:25
Supercomputing is known as a powerful tool for scientific research, but it may also come to fuel industrial innovation and serve people's daily lives, said Lu Yutong, program chair of 2019 ISC High Performance, an annual conference and exhibition on supercomputing in Europe.
"Supercomputing is no longer as lofty and away from life as people thought it was," said Lu, who is also director of the National Supercomputing Center in Guangzhou in southern China, sain in a recent interview with Xinhua.
How it will play a better role in the industrial and commercial world and serve people's daily lives is also on the conference agenda, Lu said as the much-watched supercomputing event officially opened Monday in Frankfurt, Germany, which has attracted more than 3,300 practitioners and enthusiasts worldwide of the cutting-edge supercomputing technologies.
Lu's center is home to the world's fourth fastest supercomputer, Tianhe-2A (Milky Way-2A). The system has about 3,500 direct users, from fields such as airplanes, high-speed rail, industrial design, weather forecast and biomedicine, Lu said.
Just as the flourishing of artificial intelligence (AI) relies on the improvement of computational power, the merging of supercomputing and technologies like AI and big data might as well lead to new developments in the next generation computer system, she said.
Lu described the demand for supercomputing application as "boundless."
"Supercomputing has been helping humans push the boundaries, in tasks as big as the cosmo and celestial bodies or as small as in life science, or simulate some extreme conditions. It will continue to play a role in these cutting-edge areas of scientific research," she said.
Lu believed more powerful exascale supercomputers will be needed to process the enormous quantity of data produced by various simulations nowadays or data from the internet.
Supercomputing is an integrated application of hardware, software, storage and connection technologies. "To build the fastest system, it requires each part to be the most advanced. That means more exchanges between peers (are needed) to foster a prosperous global supercomputing community," she said.
China leads the world's Top 500 supercomputer list with 219 systems, or 43.8 percent of the total, followed by the United States with 116, and Japan with 29, according to a semi-annual ranking released at 2019 ISC. The U.S.-built system Summit retains the first position.
"As more Chinese supercomputers enter the list, scientists and researchers from other parts of the world began to know about us, " Lu said.
First held in 1986 and formerly known as the International Supercomputing Conference, ISC High Performance is Europe's most important conference and networking event for the high performance computing community. The 2019 ISC event will last till Thursday.
supercat
Colonel
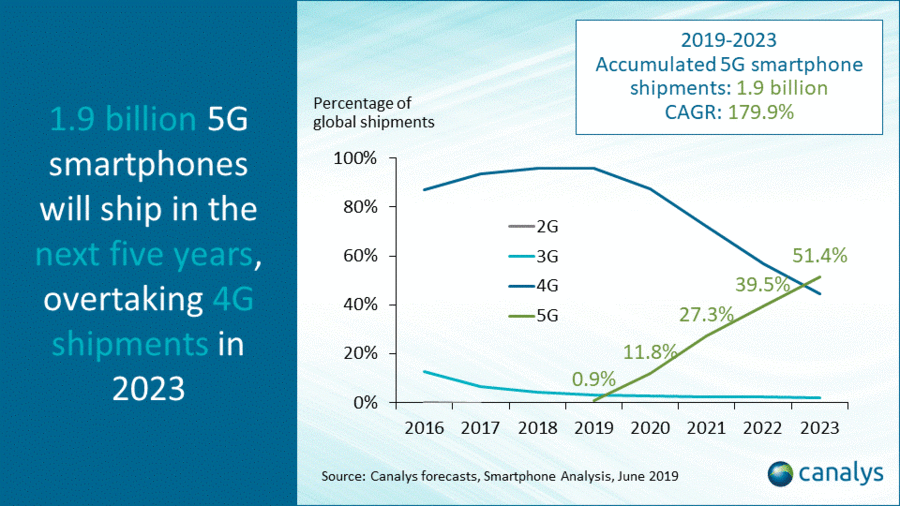
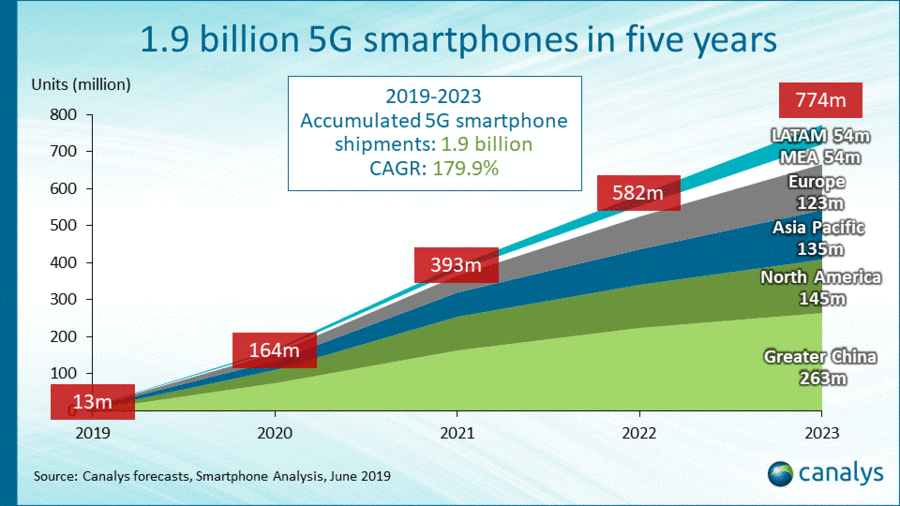
Greater China will lead 5G phone shipments to 2023:
Canalys: 1.9 billion 5G smartphones will ship in the next five years, overtaking 4G in 2023
Shanghai, Bengaluru (India), Singapore, Reading (UK) and Portland (US) – Monday, 1 July 2019
At MWC Shanghai 2019, . We expect 5G-enabled handsets will reach nearly 800 million units in 2023, accounting for 51.4% of all smartphone shipments, passing 4G smartphones five years after 5G’s global commercial launch. The CAGR between 2019 and 2023 will be 179.9%, while vendors will ship nearly 1.9 billion devices to market by the end of 2023. Greater China will account for 34.0% of 5G smartphone shipments in 2023, followed by North America at 18.8% and Asia Pacific at 17.4%.
Canalys recognizes that government initiatives to accelerate 5G development are a powerful and effective driver for faster roll-out in some markets, such as China and the US. “There was a phenomenal amount of 5G discussion at this year’s MWC Shanghai, with Chinese 5G licenses granted a year earlier than planned. The role of the Chinese government and the well-orchestrated joint investments of operators and equipment suppliers were critical to this earlier commercial launch,” said Nicole Peng, Vice President of Mobility at Canalys.
Canalys forecasts that in 2020, 17.5% of smartphones shipped in China will be 5G-capable, and this percentage will rise sharply to 62.7% in 2023. “5G smartphones will see rapid adoption in China, thanks to a strong government technology roadmap and operators’ financial capabilities. China is also home to many major 5G equipment suppliers and smartphone vendors, which will be responsible for an aggressive marketing push over the next few years,” added Peng. “But mass-market adoption of 5G smartphones does not necessarily mean a successful 5G deployment. Full 5G deployment will take much longer, and be much more complex than the previous network generation, in order to realize the benefits of 5G beyond eMBB (enhanced Mobile Broadband). And this is very costly, putting more pressure on global operators, which are already facing declining revenue and more price competition from MVNOs.”
“Chinese operators’ investments in 5G will reach US$5 billion this year, and around 70,000 to 90,000 5G base stations will be built across the country. Among the three operators, China Mobile will be extending its market advantage, given its vast user base and financial strength,” said Canalys Analyst Mo Jia. “China Mobile has the broadest 5G smartphone portfolio at launch. Given the government has just implemented the long-awaited mobile number portability policy, all three operators will be even more aggressive with promotions to target 5G early adopters and high-value customers later this year. Unsurprisingly, local Chinese brands, such as Huawei, Oppo, Xiaomi and ZTE, are 5G handset launch partners for the three operators, while Samsung will also use this window of opportunity to fight back in China. Yet Apple will miss out, leaving loyal iPhone users waiting another year, which might risk them switching to aggressive competitors,” added Jia.
