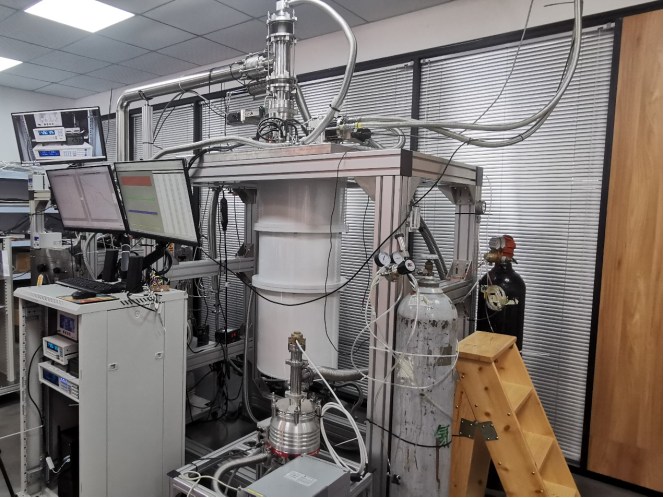
Chinese scientists discovered "the first example of a fundametally new class of photocathode quantum materials".
Paper:
News:
北京时间3月9日凌晨,相关论文《一种钙钛矿氧化物上的反常强烈相干二次光电子发射》,已提前在线发表于《自然》期刊。西湖大学博士研究生洪彩云、邹文俊和冉鹏旭为论文共同第一作者,西湖大学理学院终身副教授何睿华为通讯作者。
1887年,德国物理学家赫兹在实验中意外发现,紫外线照射到金属表面电极上会产生火花。1905年,爱因斯坦基于光的量子化猜想,提出了对该现象的理论解释。这标志着量子力学大门的正式开启。由此,将“光”转化为“电”的“光电效应”,以及能够产生这个效应的“光阴极”材料,正式进入人类的视野。
“这些光阴极材料基本上都是传统金属和半导体材料,大多数在60年前被发现。它们已成为当代粒子加速器、自由电子激光、超快电镜、高分辨电子谱仪等尖端科技装置的核心元件。”何睿华表示,然而,这些传统材料存在固有的性能缺陷——它们所发射的电子束“相干性”太差,也就是说,电子束的发射角太大,其中的电子运动速度不均一。这样的“初始”电子束要想满足尖端科技应用的要求,必须依赖一系列材料工艺和电气工程技术来增强它的相干性,而这些特殊工艺和辅助技术的引入极大地增加了“电子枪”系统的复杂度,提高了建造要求和成本。
尽管基于光阴极的电子枪技术最近几十年来有了长足的发展,但已渐渐无法跟上相关科技应用发展的步伐。许多前述尖端科技的升级换代呼唤初始电子束相干性在数量级上的提升,而这已经不是一般的光阴极性能优化所能实现的了,只能寄望于在材料和理论层面上的源头创新。
深耕材料物理性质研究的西湖大学理学院何睿华团队,意外在一个同类物理实验室中“常见”的量子材料——钛酸锶上实现了突破。
此前以钛酸锶为首的氧化物量子材料研究,主要是将这些材料当作硅基半导体的潜在替代材料来研究,但何睿华团队却通过一种强大的、但很少被应用于光阴极研究的实验手段:角分辨光电子能谱技术,出乎意料地捕捉到这些熟悉的材料竟然同样承载着触发新奇光电效应的能力——它有着远超于现有光阴极材料的光阴极关键性能:相干性,且无法为现有光电发射理论所解释。
超快电镜专家、论文合作者、西湖大学理学院研究员郑昌喜认为,合作团队的这一发现,其重要性不在于往钛酸锶的神奇性质列表增添了一个新的性质,而在于这个性质本身,它可能重启一个极其重要、被普遍认为已发展成熟的光阴极技术领域,改变许多早已根深蒂固的游戏规则。
记者了解到,接下来,该团队将在理论和应用方面开展对相关材料的进一步研究工作。
Paper:
Anomalous intense coherent secondary photoemission from a perovskite oxide
Abstract
Photocathodes—materials that convert photons into electrons using the photoelectric effect—are a critical foundation for many modern technologies that rely on light detection or electron-beam generation1,2,3. Currently existing photocathodes, however, are based on conventional metals and semiconductors that were mostly discovered six decades ago with sound theoretical underpinnings4,5. Progress in this mature field has been limited to refinements in photocathode performance based on sophisticated materials engineering1,6. Here we report unusual photoemission properties of a reconstructed surface of SrTiO3(100) single crystals prepared by simple vacuum annealing that go beyond the existing theoretical descriptions4,8,7-10. Unlike other positive-electron-affinity (PEA) photocathodes, our PEA SrTiO3 surface produces discrete secondary photoemission spectra at room temperature, characteristic of the efficient negative-electron-affinity photocathode materials11,12. At low temperatures, the photoemission peak intensity is enhanced substantially, and the electron beam obtained upon non-threshold excitations displays longitudinal and transverse coherence that shatters known records by at least an order of magnitude6,13,14. The observed emergence of coherence in secondary photoemission points to the development of an underlying novel process on top of those encompassed in the current theoretical photoemission framework. SrTiO3 thus presents the first example of a fundamentally new class of photocathode quantum materials, opening new prospects for applications that require intense coherent electron beams without the need for monochromatic excitations, electron filtering or beam acceleration.News:
世界首例!我国科学家发现光阴极“量子”材料
记者从西湖大学获悉,西湖大学理学院何睿华课题组连同研究合作者一起,发现了世界首例具有本征相干性的光阴极量子材料,其性能远超传统的光阴极材料,且无法为现有理论所解释,为光阴极研发、应用与基础理论发展打开了新的天地。北京时间3月9日凌晨,相关论文《一种钙钛矿氧化物上的反常强烈相干二次光电子发射》,已提前在线发表于《自然》期刊。西湖大学博士研究生洪彩云、邹文俊和冉鹏旭为论文共同第一作者,西湖大学理学院终身副教授何睿华为通讯作者。
1887年,德国物理学家赫兹在实验中意外发现,紫外线照射到金属表面电极上会产生火花。1905年,爱因斯坦基于光的量子化猜想,提出了对该现象的理论解释。这标志着量子力学大门的正式开启。由此,将“光”转化为“电”的“光电效应”,以及能够产生这个效应的“光阴极”材料,正式进入人类的视野。
“这些光阴极材料基本上都是传统金属和半导体材料,大多数在60年前被发现。它们已成为当代粒子加速器、自由电子激光、超快电镜、高分辨电子谱仪等尖端科技装置的核心元件。”何睿华表示,然而,这些传统材料存在固有的性能缺陷——它们所发射的电子束“相干性”太差,也就是说,电子束的发射角太大,其中的电子运动速度不均一。这样的“初始”电子束要想满足尖端科技应用的要求,必须依赖一系列材料工艺和电气工程技术来增强它的相干性,而这些特殊工艺和辅助技术的引入极大地增加了“电子枪”系统的复杂度,提高了建造要求和成本。
尽管基于光阴极的电子枪技术最近几十年来有了长足的发展,但已渐渐无法跟上相关科技应用发展的步伐。许多前述尖端科技的升级换代呼唤初始电子束相干性在数量级上的提升,而这已经不是一般的光阴极性能优化所能实现的了,只能寄望于在材料和理论层面上的源头创新。
深耕材料物理性质研究的西湖大学理学院何睿华团队,意外在一个同类物理实验室中“常见”的量子材料——钛酸锶上实现了突破。
此前以钛酸锶为首的氧化物量子材料研究,主要是将这些材料当作硅基半导体的潜在替代材料来研究,但何睿华团队却通过一种强大的、但很少被应用于光阴极研究的实验手段:角分辨光电子能谱技术,出乎意料地捕捉到这些熟悉的材料竟然同样承载着触发新奇光电效应的能力——它有着远超于现有光阴极材料的光阴极关键性能:相干性,且无法为现有光电发射理论所解释。
超快电镜专家、论文合作者、西湖大学理学院研究员郑昌喜认为,合作团队的这一发现,其重要性不在于往钛酸锶的神奇性质列表增添了一个新的性质,而在于这个性质本身,它可能重启一个极其重要、被普遍认为已发展成熟的光阴极技术领域,改变许多早已根深蒂固的游戏规则。
记者了解到,接下来,该团队将在理论和应用方面开展对相关材料的进一步研究工作。