You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
News on China's scientific and technological development.
- Thread starter Quickie
- Start date
Periodic Drive-Based Operator Propagation in Superconducting Quantum Circuits
The propagation of operators is a new perspective to study the non-equilibrium dynamics of quantum many-body systems. It is closely related to concepts such as the Lieb-Robinson bound and information scrambling in quantum chaotic systems. The fields of condensed matter physics and statistical physics have aroused great interest. The propagation of the operator can be quantified by the out-of-time-order correlator (OTOC), while the OTOC measurement requires the system to evolve backward in time, that is, to reverse the sign of the Hamiltonian, which is very important for quantum simulation. Experiments present great challenges. Periodic actuation (Floquet engineering) can be used to change the coupling between qubits and has been widely used in the coherent control of quantum systems. This method provides a possible way to realize the reverse evolution of quantum many-body systems and measure OTOC.
Recently, researchers from the Q03 group of the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences/Beijing National Research Center for Condensed Matter Physics, Fan Yu, Zhao Shiping, and Xu Kai, research fellows, SC5 group researcher Zheng Dongning, Xiang Zhongcheng, deputy chief engineer, and Beijing Institute of Quantum Information Science Researcher Yu Haifeng Together with others, the OTOC was measured for the first time in a multi-bit superconducting circuit using the periodic drive method, and the propagation properties of the operator were studied.
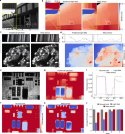
The experiment was done in a one-dimensional array of 10 superconducting qubits. By precisely regulating the AC flux bias of a specific qubit to control the coupling strength between neighboring bits, the photon quantum walk, reverse time evolution and OTOC measurement of different coupled XY models were successfully demonstrated. In the experiment, Pauli Z and X operators are selected as butterfly operators in OTOC, respectively, and these two operators are mapped into local and non-local fermion operators under the Jordan-Wigner transform. It is experimentally demonstrated that a clear cone-like operator propagation of light can be exhibited in a multi-particle system with a velocity almost equal to the group velocity of a single-photon quantum walk. The OTOC of the Pauli Z operator recovers to its initial value after a rapid decay and finally approaches zero, which describes the athermalization process in the absence of information scrambling. In contrast, for the OTOC of Pauli X, no such information recovery was observed early in evolution, showing the characteristic of information scrambling. These results elucidate different behaviors of OTOCs in near-integrable systems, some of which behave similarly to non-integrable chaotic systems.
This work was recently published as Editor's suggestion in Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 160602 (2022) under the title "Probing Operator Spreading via Floquet Engineering in a Superconducting Circuit". Doctoral students Zhao Shoukuan and Ge Ziyong (graduated) of the Q03 group and Xiang Zhongcheng, deputy chief engineer of the SC5 group, are the co-first authors. This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Beijing Natural Science Foundation, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences Pilot Project.

Cross post of new English captioned documentaries of China's recent sci-tech advancements across various fields:
Positive YouTube channels on China
Not sure where else to put this. Anyway, Condi Rice interviews Kevin Rudd about the US-China relationship. I don't think you understand what the word "Positive" means.
www.sinodefenceforum.com
News report in Chinese:
Paper in English:
上海光机所与合作单位提出紫外超连续产生新机制
近期,中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室与国防科技大学等单位合作,提出一种产生紫外超连续辐射的新机制,并将其作为探针获得了CO2隧穿电离后的吸收光谱。相关研究结果以“Ultraviolet supercontinuum generation driven by ionic coherence in a strong laser field”为题发表在Nature Communications(《自然·通讯》)上。
超连续相干光源在显微成像、分子结构分析、光化反应监测等众多科学领域具有重要应用。超连续光源一般通过激光与透明介质的非线性相互作用产生。基于自相位调制、自陡峭等传统的非线性光学效应,容易获得可见光和近红外区域的超连续光源,但紫外波段超连续产生仍具有一定的挑战性。
在本项工作中,研究团队发现利用中红外飞秒激光电离空气中普遍存在的氮分子,可以在紫外波段产生约100 nm带宽的超连续辐射,为产生短波区超连续相干光源提供了新思路。与以往的超连续产生机制不同,这种紫外超连续辐射是强场隧穿电离和光-离子多光子多通道相干耦合共同作用的结果。研究表明,在强场电离的同时,由于动态Stark效应,中红外飞秒激光可以连续改变分子离子激发态到基态的跃迁能,使得它能够与激光场发生动态五光子共振,从而诱导了分子离子能级间的量子相干。离子相干极化促使了紫外区强相干辐射的产生,其辐射波长随瞬时跃迁能的变化连续改变,因此形成了紫外超连续辐射。研究团队还揭示了多个离子态之间的协同和竞争作用对于超连续产生的重要贡献,并展示了该紫外超连续相干光在二氧化碳离子吸收光谱中的应用。
该研究打破了人们普通认为的气体介质束缚态到束缚态跃迁将产生具有孤立特征峰光谱结构的辐射的传统观念,证明了强激光可以强烈地改变量子束缚态之间的跃迁和辐射特性,为解决短波区超连续产生的难题提供了简单有效的新途径。同时,也搭建了强场物理和量子光学研究的桥梁,为开展强场离子量子光学研究提供了新机遇。
相关工作得到了国家自然科学基金重大研究计划、国家重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金、上海市优秀学术带头人、中科院青年创新促进会等项目的支持。
Paper in English:
Ultraviolet supercontinuum generation driven by ionic coherence in a strong laser field
Abstract
Supercontinuum (SC) light sources hold versatile applications in many fields ranging from imaging microscopic structural dynamics to achieving frequency comb metrology. Although such broadband light sources are readily accessible in the visible and near infrared regime, the ultraviolet (UV) extension of SC spectrum is still challenging. Here, we demonstrate that the joint contribution of strong field ionization and quantum resonance leads to the unexpected UV continuum radiation spanning the 100 nm bandwidth in molecular nitrogen ions. Quantum coherences in a bunch of ionic levels are found to be created by dynamic Stark-assisted multiphoton resonances following tunneling ionization. We show that the dynamical evolution of the coherence-enhanced polarization wave gives rise to laser-assisted continuum emission inside the laser field and free-induction decay after the laser field, which jointly contribute to the SC generation together with fifth harmonics. As proof of principle, we also show the application of the SC radiation in the absorption spectroscopy. This work offers an alternative scheme for constructing exotic SC sources, and opens up the territory of ionic quantum optics in the strong-field regime.
光学学报, 2022, 42(13): 1305002, 网络出版: 2022-07-15
极紫外光刻快速掩模优化方法
Fast Mask Optimization Method for Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography
摘要
提出了一种快速的极紫外光刻像素化掩模优化方法。优化过程中采用改进的像素化快速厚掩模模型,根据掩模像素尺寸设置边界像素上点脉冲的大小。以双重边界演化方法为基础,在每轮优化时,根据当前光刻胶轮廓与目标图形轮廓的差异自适应地对优化变量进行初始化,利用先验信息生成初始个体和种群,从而提高优化效率。以一维线空图形和二维复杂图形为例进行了仿真验证,结果表明该方法有效提高了掩模成像仿真精度,两种二维掩模图形的优化效率得到明显提高。
Abstract
This paper proposes a fast pixelated mask optimization method for extreme ultraviolet lithography. An improved fast pixelated thick mask model is utilized in mask optimization. The point pulses on the edge pixels are set according to the mask pixel size. On the basis of the dual edge evolution strategy, the optimization variables are adaptively initialized in each epoch of optimization according to the difference between the current resist pattern contour and the target pattern contour. The optimization efficiency is improved by generating the initial individuals and population using priori information. One-dimensional line-space patterns and two-dimensional complex patterns are used for simulation. Simulation results show that the imaging simulation accuracy is effectively improved. In addition, the optimization efficiency of the two complex patterns is effectively increased by the proposed method.
Scientists from Tsinghua created a meta-imaging sensor that can "realize perfect optical imaging in 3D (实现完美的三维光学成像)".
"Here we propose an integrated scanning light-field imaging sensor, termed a meta-imaging sensor, to achieve high-speed aberration-corrected three-dimensional photography for universal applications without additional hardware modifications."
"Using the sensor, we achieve high-performance photography up to a gigapixel with a single spherical lens without a data prior, leading to orders-of-magnitude reductions in system capacity and costs for optical imaging."
"Moreover, high-density accurate depth maps can be retrieved simultaneously, facilitating diverse applications from autonomous driving to industrial inspections."
The lead scientist first brough up the idea of "self adaptive digital optics" in 2021 in an paper published on Cell. Now the team has integrated everything in a single imagine chip that can be used in almost all imaging applications, without modifying the existing imaging system.
Paper published in English (not paywalled at the moment):
News release in Chinese:
"Here we propose an integrated scanning light-field imaging sensor, termed a meta-imaging sensor, to achieve high-speed aberration-corrected three-dimensional photography for universal applications without additional hardware modifications."
"Using the sensor, we achieve high-performance photography up to a gigapixel with a single spherical lens without a data prior, leading to orders-of-magnitude reductions in system capacity and costs for optical imaging."
"Moreover, high-density accurate depth maps can be retrieved simultaneously, facilitating diverse applications from autonomous driving to industrial inspections."
The lead scientist first brough up the idea of "self adaptive digital optics" in 2021 in an paper published on Cell. Now the team has integrated everything in a single imagine chip that can be used in almost all imaging applications, without modifying the existing imaging system.
Paper published in English (not paywalled at the moment):
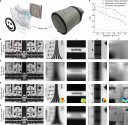
An integrated imaging sensor for aberration-corrected 3D photography
Abstract
Planar digital image sensors facilitate broad applications in a wide range of areas,,,,, and the number of pixels has scaled up rapidly in recent years,. However, the practical performance of imaging systems is fundamentally limited by spatially nonuniform optical aberrations originating from imperfect lenses or environmental disturbances,. Here we propose an integrated scanning light-field imaging sensor, termed a meta-imaging sensor, to achieve high-speed aberration-corrected three-dimensional photography for universal applications without additional hardware modifications. Instead of directly detecting a two-dimensional intensity projection, the meta-imaging sensor captures extra-fine four-dimensional light-field distributions through a vibrating coded microlens array, enabling flexible and precise synthesis of complex-field-modulated images in post-processing. Using the sensor, we achieve high-performance photography up to a gigapixel with a single spherical lens without a data prior, leading to orders-of-magnitude reductions in system capacity and costs for optical imaging. Even in the presence of dynamic atmosphere turbulence, the meta-imaging sensor enables multisite aberration correction across 1,000 arcseconds on an 80-centimetre ground-based telescope without reducing the acquisition speed, paving the way for high-resolution synoptic sky surveys. Moreover, high-density accurate depth maps can be retrieved simultaneously, facilitating diverse applications from autonomous driving to industrial inspections.
News release in Chinese:
清华新闻网10月20日电 完美光学成像是人类感知世界的终极目标之一,但这个目标却从根本上受制于镜面加工误差与复杂环境扰动所引起的光学像差。《科学》期刊也将“能否制造完美的光学透镜”列为21世纪125个科学前沿问题之一。
近日,清华大学成像与智能技术实验室提出了一种集成化的元成像芯片架构(Meta-imaging sensor),为解决这一百年难题开辟了一条新路径。区别于构建完美透镜,研究团队另辟蹊径,研制了一种超级传感器,记录成像过程而非图像本身,通过实现对非相干复杂光场的超精细感知与融合,即使经过不完美的光学透镜与复杂的成像环境,依然能够实现完美的三维光学成像。团队攻克了超精细光场感知与超精细光场融合两大核心技术,以分布式感知突破空间带宽积瓶颈,以自组织融合实现多维多尺度高分辨重建,借此能够用对光线的数字调制来替代传统光学系统中的物理模拟调制,并将其精度提升至光学衍射极限。这一技术解决了长期以来的光学像差瓶颈,有望成为下一代通用像感器架构,而无需改变现有的光学成像系统,带来颠覆性的变化,将应用于天文观测、生物成像、医疗诊断、移动终端、工业检测、安防监控等领域。
传统光学系统主要为人眼所设计,保持着“所见即所得”的设计理念,聚焦于在光学端实现完美成像。近百年来,光学科学家与工程师不断提出新的光学设计方法,为不同成像系统定制复杂的多级镜面、非球面与自由曲面镜头,来减小像差提升成像性能。但由于加工工艺的限制与复杂环境的扰动,难以制造出完美的成像系统。例如由于大范围面形平整度的加工误差,难以制造超大口径的镜片实现超远距离高分辨率成像;地基天文望远镜,受到动态变化的大气湍流扰动,实际成像分辨率远低于光学衍射极限,限制了人类探索宇宙的能力,往往需要花费昂贵的代价发射太空望远镜绕过大气层。
为了解决这一难题,自适应光学技术应运而生,人们通过波前传感器实时感知环境像差扰动,并反馈给一面可变形的反射镜阵列,动态矫正对应的光学像差,以此保持完美的成像过程,基于此人们发现了星系中心的巨大黑洞并获得了诺贝尔奖,并广泛应用于天文学与生命科学领域。然而由于像差在空间分布非均一的特性,该技术仅能实现极小视场的高分辨成像,而难以实现大视场多区域的同时矫正,并且由于需要非常精细的复杂系统往往成本十分高昂。
早在2021年,自动化系戴琼海院士领导的成像与智能实验技术实验室研究团队发表于《细胞》期刊上的工作,首次提出了数字自适应光学的概念,为解决空间非一致的光学像差提供了新思路。在最新的研究成果中,研究团队将所有技术集成在单个成像芯片上,使之能广泛应用于几乎所有的成像场景,而不需要对现有成像系统做额外的改造,并建立了波动光学范畴下的数字自适应光学架构。通过对复杂光场的高维超精细感知与融合,在具备极大的灵活性的同时,又能保持前所未有的成像精度。这一优势使得在数字端对复杂光场的操控能够完全媲美物理世界的模拟调制,就好像人们真正能够在数字世界搬移每一条光线一样,将感知与矫正的过程完全解耦开来,从而能够同时实现不同区域的高性能像差矫正。
传统相机镜头的成本和尺寸都会随着有效像素数的增加而迅速增长,这也是为什么高分辨率手机成像镜头即使使用了非常复杂的工艺也很难变薄,高端单反镜头特别昂贵的原因。因为它们通常需要多个精密设计与加工的多级镜片来校正空间不一致的光学像差,而如果想进一步推进到有效的十亿像素成像对传统光学设计来说几乎是一场灾难。元成像芯片从底层传感器端为这些问题提供了可扩展的分布式解决方案,使得我们能够使用非常简易的光学系统实现高性能成像。在普通的单透镜系统上即可通过数字自适应光学实现了十亿像素高分辨率成像,将光学系统的成本与尺寸降低了三个数量级以上。
除了成像系统存在的系统像差以外,成像环境中的扰动也会导致空间折射率的非均匀分布,从而引起复杂多变的环境像差。其中最为典型的是大气湍流对地基天文望远镜的影响,从根本上限制了人类地基的光学观测分辨率,迫使人们不得不花费高昂的代价发射太空望远镜,比如价值百亿美元的韦伯望远镜。硬件自适应光学技术虽然可以缓解这一问题并已经被广泛使用,但它设计复杂、成本高昂,并且有效视野直径通常都小于40角秒。数字自适应光学技术仅仅需要将传统成像传感器替换为元成像芯片,就能为大口径地基天文望远镜提供全视场动态像差矫正的能力。研究团队在中国国家天文台兴隆观测站上的清华-NAOC 80厘米口径望远镜上进行了测试,元成像芯片显著提升了天文成像的分辨率与信噪比,将自适应光学矫正视场直径从40角秒提升至了1000角秒。
元成像芯片还可以同时获取深度信息,比传统光场成像方法在横向和轴向都具有更高的定位精度,为自动驾驶与工业检测提供了一种低成本的解决方案。未来,课题组将进一步深入研究元成像架构,充分发挥元成像在不同领域的优越性,建立新一代通用像感器架构,从而带来三维感知性能的颠覆性提升,或可广泛用于天文观测、工业检测、移动终端、安防监控、医疗诊断等领域。
该成果于10月19日以“集成化成像芯片实现像差矫正的三维摄影”(An integrated imaging sensor for aberration-corrected 3D photography)为题以长文(Article)的形式发表在《自然》(Nature)期刊上。
清华大学自动化系戴琼海院士、电子系方璐副教授为该论文共同通讯作者;自动化系吴嘉敏助理教授、清华-伯克利深圳学院2020级博士研究生郭钰铎、自动化系博士后邓超担任共同第一作者。自动化系乔晖助理教授以及清华-伯克利深圳学院2018级博士研究生张安科、清华大学自动化系2018级博士研究生卢志、清华大学自动化系2020级博士研究生谢佳辰共同参与了该研究。该研究受到了国家自然科学基金委与国家科技部的资助。
Attachments
50 minute CCTV documentary about recent key Chinese advances in telecom and semiconductor industries, ENG captions available. Domestic optical fibre, 5G, 7 nm chip manufacture, FOLED, image recognition/surveillance, automation and smart logistics, cybersecurity are the topics covered.
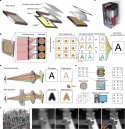
Challenges and strategies in high-accuracy manufacturing of the world’s largest SiC aspheric mirror
Abstract
In the process of manufacturing the world’s largest silicon carbide (SiC) aspheric mirror, the primary difficulties are mirror blank preparation, asphere fabrication, and testing, as well as cladding and coating. Specifically, the challenges include the homogeneity of the complicated structure casting, accuracy and efficiency of the fabrication process, print-through effect, fidelity and precision of test procedure, stress and denseness of cladding process, the dynamic range of interferometric measurement, and air turbulence error due to the long optical path. To break through such a barrier of difficulties, we proposed the water-soluble room temperature vanishing mold and gel casting technology, homogeneous microstructure reaction-formed joint technology, nano-accuracy efficient compound fabrication, gravity unloading technology, high-denseness low-defect physical vapor deposition (PVD) Si-cladding technology, test data fusion method, and time-domain averaging method, etc. Based on the proposed technologies and methods, we have accomplished the world’s largest SiC aspheric mirror with a size of ⌀4.03 m. The impressive performance of the SiC aspheric mirror is validated by the characteristics of the fabricated SiC aspheric mirror. The aerial density of the SiC blank is less than 120 kg/m2, surface shape test accuracy is better than 6 nm RMS, thickness inhomogeneity of the cladding layer is less than 5%, and the final surface figure error and roughness are 15.2 nm RMS and 0.8 nm RMS, respectively.
This could be used to develop big EUV mirrors.