by78
General
Timeline for the Tianwen-3 mars sample return mission has been shifted to the right. It's now expected to be launched around 2030.

Another slide on Mars exploration missions into the 2050s.
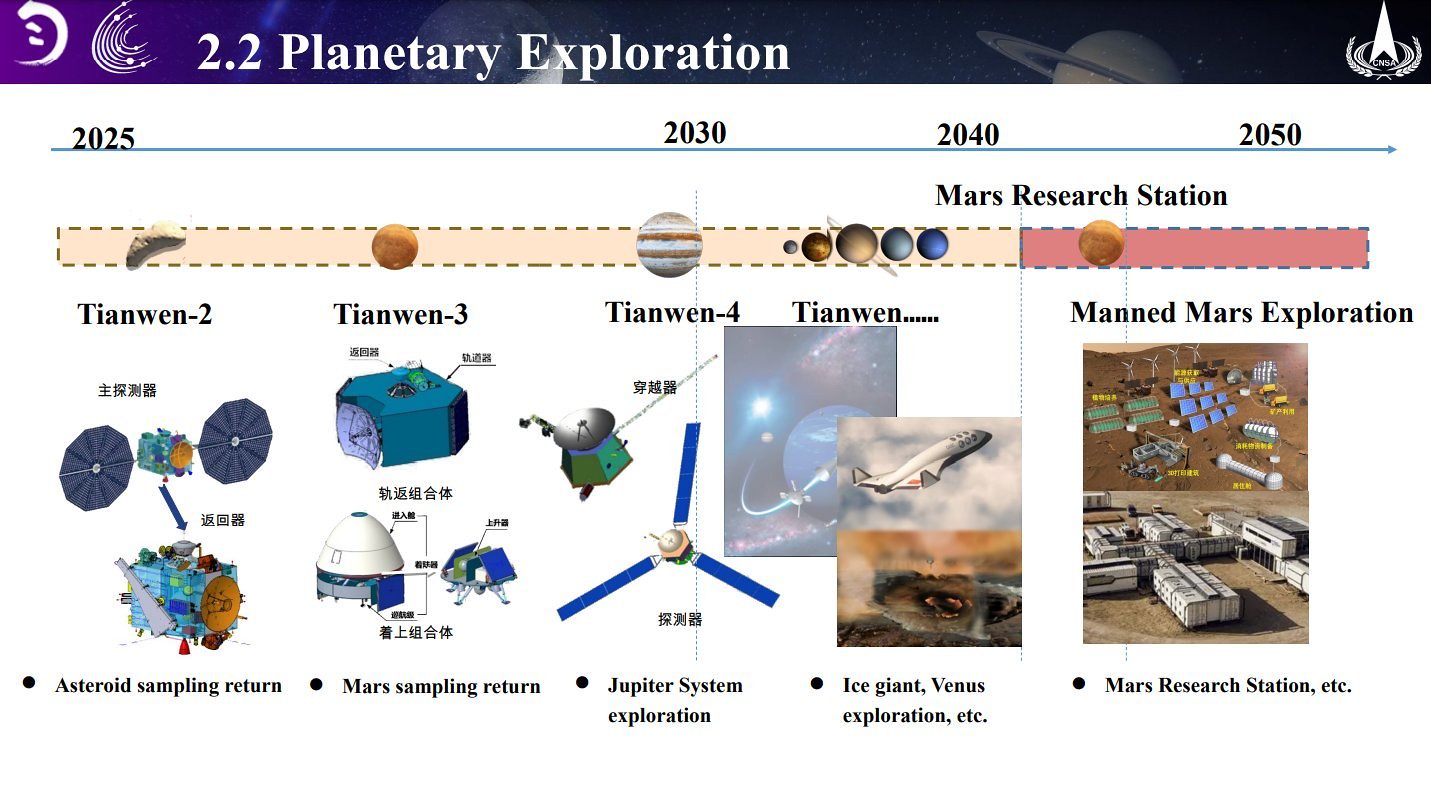
Timeline for the Tianwen-3 mars sample return mission has been shifted to the right. It's now expected to be launched around 2030.







The private startup Beijing Arrowhead/Space Epoch (箭元科技公司) has successfully conducted a splashdown test of its reusable LOX/Methane XZY-1 rocket. The first stage of the rocket –– encased in stainless steel –– was dropped into sea water to simulate landing impact and was subsequently recovered. After cleaning and inspection, all systems and components (nozzles, engine, fuel tank, servos, etc.) remained in satisfactory condition, and the first stage can be re-used.
Next, the company plans to conduct a splashdown and towed recovery test in the open ocean by mid-2024. If that test is successful, a sub-orbital launch, splashdown, and towed recovery test will follow by the end of 2024.

Some presentation slides from the private launch provider Galactic Energy.
Pallas-1A has finished assembly, first launch is expected later this year:
– Diameter: 3.35m
– Mass at take-off: 283 tons
– Capacity to LEO: 8 tons, 10 tons with optional second stage.
– Reusable first stage powered by seven engines, launch can proceed with one engine out.
Pallas-1B:
– Mass at take-off: 730 tons
– Capacity (LEO): 17.5 tons
Another interesting tidbit, which is not seen in the slides but apparently mentioned by the presenter: Galactic Energy and partners are exploring launch (assist) methods such as electromagnetic launching and pneumatic launching using supercritical carbon dioxide.





Some illustrations from a on the optimal (emergency) landing method for the return capsule of the next-generation manned spacecraft. The detail of note is that the return capsule has six cylindrical airbags for soft landing.




