You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
China's Space Program News Thread
- Thread starter crazyinsane105
- Start date
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
One of the two satellites launched by the Kuizhou-1A (KZ-1A) rocket on Sept 6, 2022 is built by Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT). The S4 satellite is the fourth experimental satellite for the low orbit GNSS enhancement system (“微厘空间“低轨卫星导航增强系统). This is the first navigation satellite built by HIT.
The S4 satellite will test space-ground integrated network control, satellite-borne micro-force high-precision electric propulsion, high precision enhanced GNSS signal broadcast, etc.
The whole GNSS enhancement system will be consist of a constellation of 160 low orbit satellites in space, and base stations on ground. It will enhance the performance of Beidou GNSS to provide global navigation info at the decimeter and centimeter level in realtime.
中新网哈尔滨9月6日电 (记者 史轶夫)哈尔滨工业大学(以下简称哈工大)6日发布消息,当日10时24分30秒,快舟一号甲固体运载火箭在酒泉卫星发射中心点火升空,以“一箭双星”方式,将“微厘空间”低轨卫星导航增强系统S3/S4试验卫星送入预定轨道,发射任务取得圆满成功。S4试验卫星是哈工大研制的首颗导航卫星,标志该校小卫星研究跨入导航卫星领域,实现新的突破。
此次发射的S4试验卫星由哈工大与哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司联合研制,是中国正在研发的低轨卫星导航增强系统演示验证任务第四颗试验卫星。
S4试验卫星将开展星地一体化组网控制管理、星载微推力高精度电推进、高精度导航增强信号播发等系列在轨技术试验和系统演示验证,为低轨卫星导航增强系统组网建设奠定基础。
“微厘空间”低轨卫星导航增强系统是由160颗低轨卫星及地面系统构成的天地一体化星座系统,对中国北斗等卫星导航系统进行性能增强,可为全球大众消费、自动驾驶、地理信息、公共安全等泛在用户提供高精度、快收敛、低成本、高可靠的卫星定位增强服务,实现全球分米(厘米)级实时动态快速导航定位。
以S4试验卫星在轨系统级演示验证为基础,哈工大联合哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司共同承担了“微厘空间”低轨卫星导航增强系统组网卫星研制任务。
The S4 satellite will test space-ground integrated network control, satellite-borne micro-force high-precision electric propulsion, high precision enhanced GNSS signal broadcast, etc.
The whole GNSS enhancement system will be consist of a constellation of 160 low orbit satellites in space, and base stations on ground. It will enhance the performance of Beidou GNSS to provide global navigation info at the decimeter and centimeter level in realtime.
哈工大研制首颗导航卫星成功发射
中新网哈尔滨9月6日电 (记者 史轶夫)哈尔滨工业大学(以下简称哈工大)6日发布消息,当日10时24分30秒,快舟一号甲固体运载火箭在酒泉卫星发射中心点火升空,以“一箭双星”方式,将“微厘空间”低轨卫星导航增强系统S3/S4试验卫星送入预定轨道,发射任务取得圆满成功。S4试验卫星是哈工大研制的首颗导航卫星,标志该校小卫星研究跨入导航卫星领域,实现新的突破。
此次发射的S4试验卫星由哈工大与哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司联合研制,是中国正在研发的低轨卫星导航增强系统演示验证任务第四颗试验卫星。
S4试验卫星将开展星地一体化组网控制管理、星载微推力高精度电推进、高精度导航增强信号播发等系列在轨技术试验和系统演示验证,为低轨卫星导航增强系统组网建设奠定基础。
“微厘空间”低轨卫星导航增强系统是由160颗低轨卫星及地面系统构成的天地一体化星座系统,对中国北斗等卫星导航系统进行性能增强,可为全球大众消费、自动驾驶、地理信息、公共安全等泛在用户提供高精度、快收敛、低成本、高可靠的卫星定位增强服务,实现全球分米(厘米)级实时动态快速导航定位。
以S4试验卫星在轨系统级演示验证为基础,哈工大联合哈尔滨工大卫星技术有限公司共同承担了“微厘空间”低轨卫星导航增强系统组网卫星研制任务。
Chinese scientists for the first time discover a new mineral on moon; new mineral named Changesite-(Y)
By Ma Jun Published: Sep 09, 2022 09:31 AM

Photo: CCTV
Chinese scientists have for the first time discovered a new mineral on the Moon, making China the third country to discover a new mineral on the moon, Chinese authority said on Friday.
Dong Baotong, vice chairman of the China Atomic Energy Authority, announced the name of the new mineral as Changesite-(Y) at Friday's press conference.
Changesite-(Y) is a phosphate mineral in columnar crystal found in lunar basalt particles. Scientists from Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology isolated a single crystal particle with a radius of about 10 microns through high-tech means such as X-ray diffraction from the 140,000 lunar sample particles, and interpreted its crystal structure.
The Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification (CNMNC) of the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) confirmed it as a new mineral.
It is the sixth new mineral discovered by humanity on the moon, and China becomes the third country in the world after the US and the former Soviet Union to discover a new mineral on the Moon.
China's Chang'e-5 mission retrieved samples from the Moon weighing about 1,731 grams in 2020, which were the first lunar samples in the world in over 40 years.
Scientists from several departments including Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ministry of Education and Ministry of Natural Resources were involved in the research of the Moon samples, and the achievements they have made so far have important implications for understanding the origin and evolution of the Moon and exploring the effective utilization of lunar resources.
By Ma Jun Published: Sep 09, 2022 09:31 AM

Photo: CCTV
Chinese scientists have for the first time discovered a new mineral on the Moon, making China the third country to discover a new mineral on the moon, Chinese authority said on Friday.
Dong Baotong, vice chairman of the China Atomic Energy Authority, announced the name of the new mineral as Changesite-(Y) at Friday's press conference.
Changesite-(Y) is a phosphate mineral in columnar crystal found in lunar basalt particles. Scientists from Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology isolated a single crystal particle with a radius of about 10 microns through high-tech means such as X-ray diffraction from the 140,000 lunar sample particles, and interpreted its crystal structure.
The Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification (CNMNC) of the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) confirmed it as a new mineral.
It is the sixth new mineral discovered by humanity on the moon, and China becomes the third country in the world after the US and the former Soviet Union to discover a new mineral on the Moon.
China's Chang'e-5 mission retrieved samples from the Moon weighing about 1,731 grams in 2020, which were the first lunar samples in the world in over 40 years.
Scientists from several departments including Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ministry of Education and Ministry of Natural Resources were involved in the research of the Moon samples, and the achievements they have made so far have important implications for understanding the origin and evolution of the Moon and exploring the effective utilization of lunar resources.
Video report on this latest discovery on CCTVChinese scientists for the first time discover a new mineral on moon; new mineral named Changesite-(Y)
By Ma Jun Published: Sep 09, 2022 09:31 AM

Photo: CCTV
Chinese scientists have for the first time discovered a new mineral on the Moon, making China the third country to discover a new mineral on the moon, Chinese authority said on Friday.
Dong Baotong, vice chairman of the China Atomic Energy Authority, announced the name of the new mineral as Changesite-(Y) at Friday's press conference.
Changesite-(Y) is a phosphate mineral in columnar crystal found in lunar basalt particles. Scientists from Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology isolated a single crystal particle with a radius of about 10 microns through high-tech means such as X-ray diffraction from the 140,000 lunar sample particles, and interpreted its crystal structure.
The Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification (CNMNC) of the International Mineralogical Association (IMA) confirmed it as a new mineral.
It is the sixth new mineral discovered by humanity on the moon, and China becomes the third country in the world after the US and the former Soviet Union to discover a new mineral on the Moon.
China's Chang'e-5 mission retrieved samples from the Moon weighing about 1,731 grams in 2020, which were the first lunar samples in the world in over 40 years.
Scientists from several departments including Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ministry of Education and Ministry of Natural Resources were involved in the research of the Moon samples, and the achievements they have made so far have important implications for understanding the origin and evolution of the Moon and exploring the effective utilization of lunar resources.
Chinese atomic clock trio bound for Tiangong space station in boost to GPS, dark matter probes
- Devices of exceptional accuracy seen to have profound implications for GPS, national defence, deep space exploration and fundamental physics research
- System will be about thousands of times more accurate than clocks on navigation satellites, China’s top space scientist says
China will soon send a trio of atomic clocks to its Tiangong space station, to establish a space-based of exceptional accuracy.
The clocks can work together to measure time with 10-17 stability – or missing one second every few billion years – the chief scientist of the Chinese crewed space programme said.
The devices have been packed inside a pair of fridge-sized cabins and are waiting to lift off from the Wenchang spaceport in southern China in October, Gu Yidong told a recent national space science assembly in Taiyuan.
The system will be about three orders of magnitude – or thousands of times – more accurate than the hydrogen maser (an acronym for microwave amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) clocks on navigation satellites.
They will have profound implications for hyper- accurate positioning, national defence, deep space exploration, and fundamental physics research, Gu said.
Atomic clocks are the most precise timepieces in the world, using lasers to measure the vibration of atoms – whose electrons jump back and forth between energy states like tiny pendulums swinging in sync.
Such clocks are the most important component of a navigation satellite, each of which contains multiple atomic devices contributing very precise time data to the positioning signals.
The best lab-based atomic clocks are so accurate that if they had been running since the beginning of the universe, they would be off by less than half a second now.
However, it is a mammoth task to downsize such clocks before sending them into space. Space-based atomic clocks need to be compact in size and robust in performance, requiring more sophisticated design and technology than those in laboratories.
In 2016, China launched the world’s first space-based, microwave cold-atom clock on board its space lab Tiangong 2.
The clock used laser beams to trap, cool and probe rubidium atoms to measure time at a few millionths of a degree above absolute zero.
Developed by physicist Liu Liang and his colleagues at the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, the clock was packed inside a box that could fit into the back of a car and operated in orbit for 34 months straight.
The new clocks on the under-construction Tiangong space station will include a rubidium microwave cold-atom clock, a strontium optical cold-atom clock, and an active hydrogen maser, Gu said.
Of these, the optical clock was developed by the National Time Service Centre in Xian in northwest China, and will be the first of its kind to be sent into space.
Elements including rubidium, strontium and caesium are the preferred choice of scientists for making atomic clocks because they are relatively stable and their vibrations are easier to observe, among other reasons.
The three clocks bound for the Tiangong space station can work independently and compare readings with each other to measure time with unprecedented accuracy.
Tests went well on the ground, and the clocks’ performance may be further improved once they become operational in space, Gu said.
The devices represent the most complex and expensive research cabins on the space station, and will also be used to test fundamental physics, helping scientists make more precise measurements of constants, look for and dark energy, and probe the merger of black holes in the distant universe.
The clocks and six other cabins will ride with the Mengtian experimental module to dock with the Tiangong next month, of the T-shaped space station.
Meanwhile, Liu’s team in Shanghai has been working on an ultra-precise cold-atom clock based on an unconventional laser cooling technology, which can further downsize the device to the dimensions of a shoebox.
Their 28kg (62lb), 70-watt rubidium diffuse laser clock will be launched next year, and is expected to improve the positioning accuracy of the BeiDou navigation satellites if all goes well, Liu told the meeting last month in Taiyuan, in central Shanxi province.
The clock on the Tiangong 2 was 1 metre by 0.5m (3.3 feet by 1.6 feet), while the new diffuse laser clock will be 0.3m by 0.4m, a significant reduction given its highly complex internal structure.
Any idea what Object G is? That's very unusual height, it looked like it was either experiencing a lot of drag or actively trying to deorbit itself over a number of weeks then it suddenly stopped and started maintaining altitude?
by78
General
The private launch vehicle company LandSpace has released a new company logo and more information on its Zhuque-2 rocket and Tianque Lox/Methane engine.
The Suzaku-2 rocket is 49.5 meters long with a body diameter of 3.35 meters. It weighs 216 tons, with a take-off thrust of 268 tons. It can carry six tons of payload to LEO and four tons to SSO.
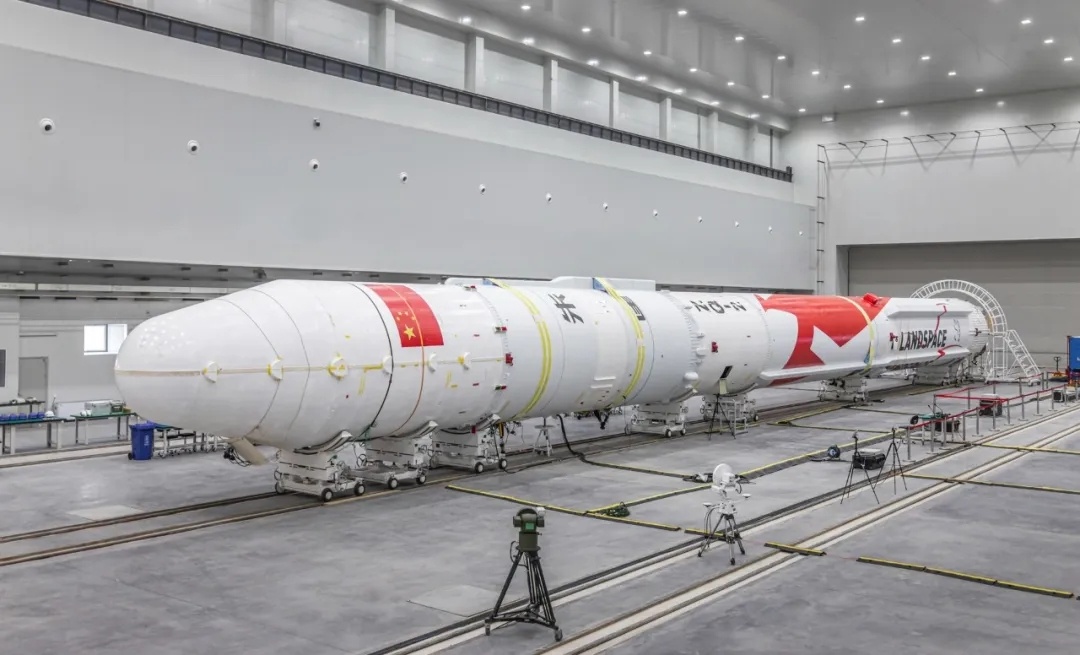
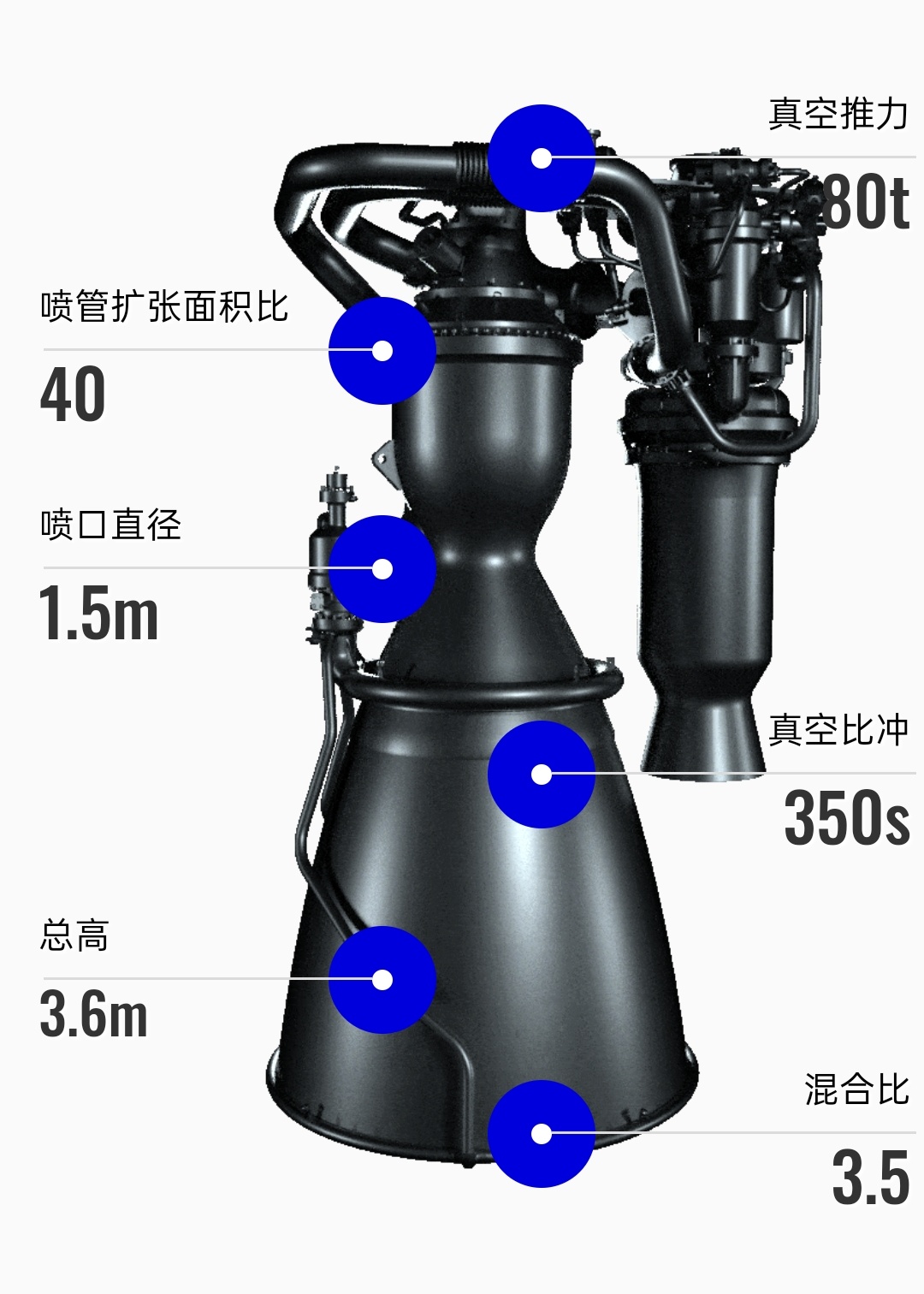



The Zhuque-2 rocket in an upright position. The launch might take place soon. I'm really looking forward to this one.

Last edited:
来自国家航天局的消息,我国探月工程有了新的进展。探月与航天工程中心主任刘继忠在接受总台记者采访时表示:探月工程四期任务已获国家批复,目前进展顺利。 探月工程四期包括嫦娥六号、嫦娥七号和嫦娥八号任务,这三个任务将在未来十年之内陆续实施。其中,嫦娥六号是嫦娥五号的备份,具备采样返回的功能,它将前往月球背面执行任务。
China Central Television interviewed with Liu Jizhong, director of the China Lunar Exploration and Aerospace Engineering Center recently.
Liu announced that the China Lunar Exploration Project phase IV was approved by the State Council and the team is heading for the project.
CLEP phase IV includes Chang'e-6, Chang'e-7 and Chang'e-8 missions and will be achieved in the next 10 years.
Chang'e-6 is the backup project of the Chang'e-5 sample-and-return project. The Chang'e-6 spacecraft is almost manufactured now.
Chang'e-6 will landed at the far side of the moon and execute another sample-and-return task.
Chang'e-7 and -8 spacecrafts are still under develop.
Chang'e-7 project will land a rover at the south pole of the moon and then survey, measure, research and choose the site for the future International Lunar Research Station.
Chang'e-8 project will build the basic structure of the International Lunar Research Station.
p.s.: Today's news.
Will manned lunar landing be before or after 2030?
- Status
- Not open for further replies.

