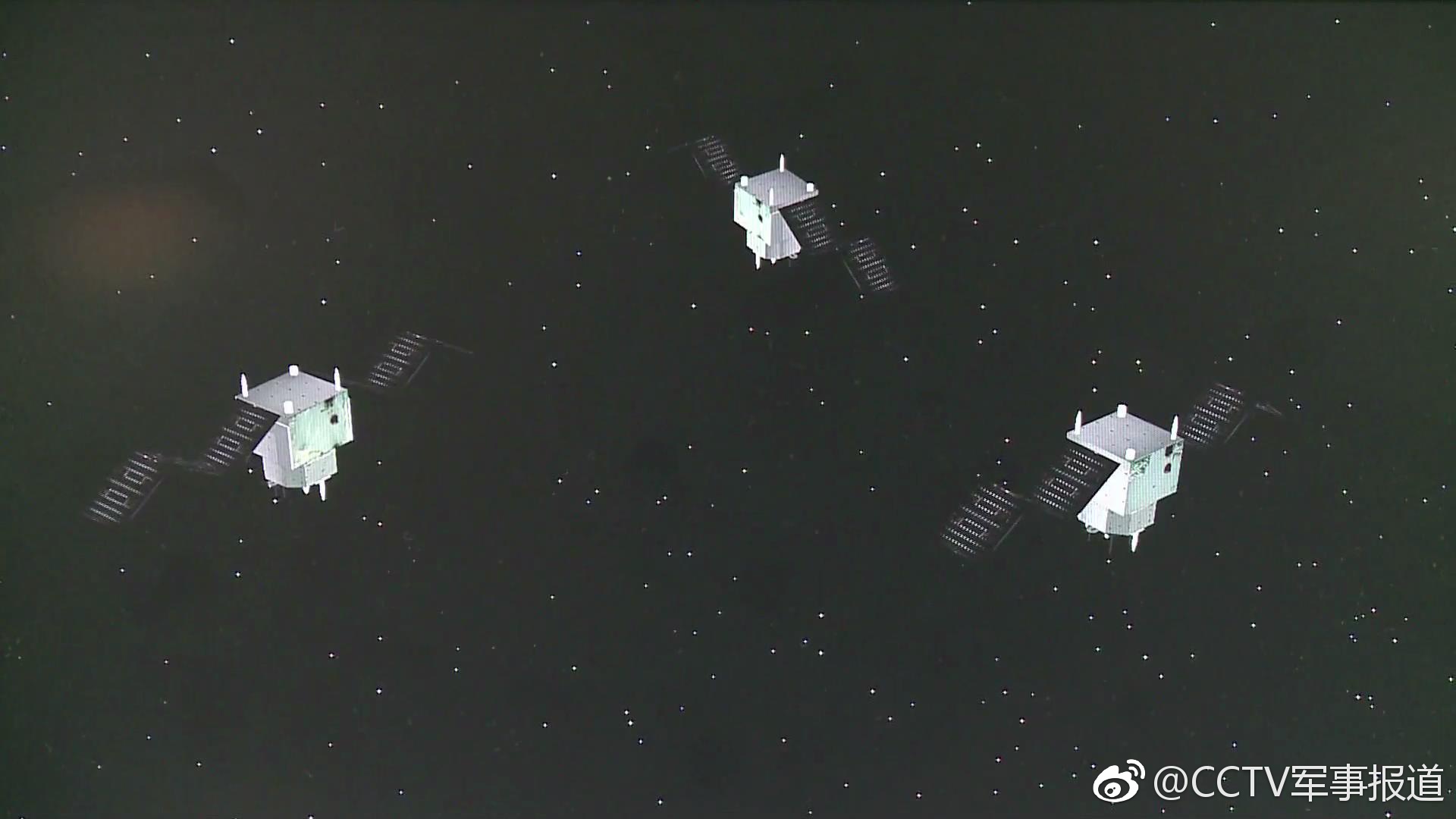
Another YG-30 triplet put into orbit to locate aircraft carriers
BY
China yesterday made its fourth space launch of the month by putting into orbit another triplet of
YG-30 military satellites . The
CZ-2C rocket took off at 2:10 am local time at the Xichang Space Center, in the middle of mountain ranges in China's Sichuan Province.
Officially, this second group of YG-30 satellites will be devoted to the analysis of the electromagnetic environment in orbit and associated technology testing, but just like the first group of three other satellites launched in late September this year, it is thought that it is actually a new family of Chinese military reconnaissance satellites, responsible for determining the position and movements of enemy military fleets through the use of wiretapping, like the
Naval Ocean Surveillance System (NOSS). ) of the US Army.
The start
Developed by the Chinese Academy of Launch Technology (CALT), a subsidiary of the Chinese aerospace group CASC, the CZ-2C is a two-stage liquid propellant launcher specializing in low-Earth-orbit (LEO) and sun-synchronous orbit launches (SSO).
It is an "old" generation launcher using hypergolic propellants, which is 43.72 meters high and 245 tons on take-off, and capable of placing up to 3,300 kg in Circular LEO orbit 300 km × 29 ° from the Xichang Space Center (XSLC).
Thirteen Chinese satellites with return capsules, US
Iridium satellites , as well as several Chinese military and experimental satellites have already been launched thanks to the CZ-2C, which now has 42 hits on 43 flight missions made public.
The launcher's only failure was on August 18, 2011 during the launch of the
SJ-11-04 military satellite . A mechanical failure of the 2nd floor would be questioned.
The CZ-2C is also used as a carrier rocket for various military engines, such as the
DF-ZF hypersonic glider for its last seven tests. Which is not surprising in itself when we know that it is derived directly from the Chinese ICBM missile DF-5.
The launch of the triplet YG-30 Group 02 (遥感 30 号 02 组) took place this Saturday, September 29th at 02: 10: 05.130 local time precisely, on the launch pad n ° 3 of XSLC. This shot that is used to accommodate larger rockets such as the CZ-3 will remain in this technical state, configured to support the CZ-2C, at least until the Chinese New Year in 2018.
The CZ-2C is the only launcher ever launched from the three Chinese space centers TSLC, JSLC and XSLC (but not yet at WSLC, the new and 4th Chinese space center on Hainan Island).
The rocket CZ-2C Y30 on the shooting pad n ° 3 in the center XSLC
As with the first triplet launch two months ago, the CZ-2C designers have designed a new under-head bracket to fix the three satellites. This new configuration will be integrated elsewhere in the "V4.0" plan that the CALT institute has planned to extend the already very long career of the rocket.
The aim is to further reduce the CZ-2C preparation cycle and makes him a reliable vector, responsive and very cheap for small satellites, including those that are too large for new launchers solid propellant as
CZ- 11 and
KZ-1A .
Content of the XSLC center's geographical location, which is entering the high-altitude high-altitude season, the engineers have also reprogrammed the CNG system to alleviate this problem, plus others that come from higher humidity levels in a very hot area. stormy.
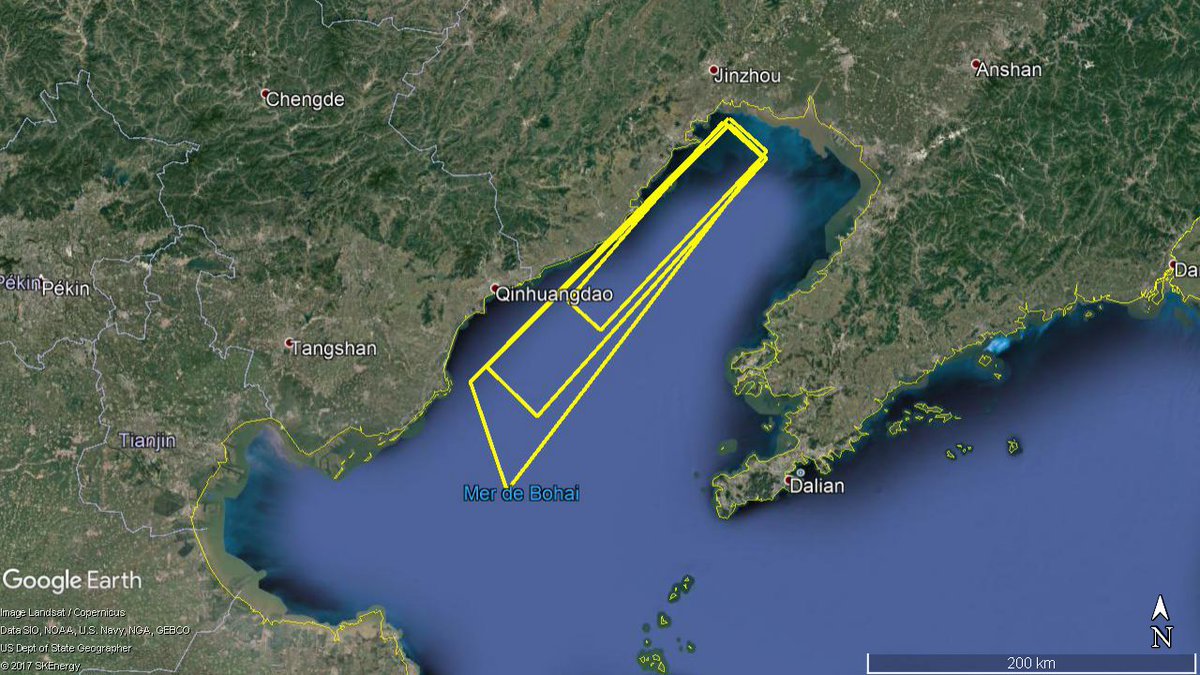
A single message to aircrafts was created to signal a fallout area in the very center of the mountainous Guizhou Province, the local government of Yangshan, a county in northern Guangdong Province, also warned its residents risk of falling caps in the vicinity.
A3444 / 17
Q) ZPKM / QRTCA / IV / BO / W / 000/999 / 2647N10713E015
A) ZPKM B) 1711241800 C) 1711241827
E) A TEMPORARY RESTRICTED AREA ESTABLISHED BOUNDED BY:
N263510E1072251-N264300E1065708-N265820E1070259-N265028E1072844
BACK TO START. VERTICAL LIMITS: GND-UNL.
F) GND G) UNL
Flight Direction and Fallout Zones Reported for Launch of YG-30 Group 02 (Image: East Pendulum)
According to NORAD data, the three satellites were injected into an orbit of 590 km × 604 km × 35 °, with a periodicity of 96.62 min. This orbital plane makes an angle of 120 ° with that of the YG-30 Group 01 triplet launched in late September, so it lacks at least one other launch, offset by 120 ° again, to have a total coverage of the globe.
A fourth object has also been listed by NORAD which is the last stage of the rocket.
OBJECT A
1 43028U 17075A 17329.08402438 -.00000027 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9997
2 43028 34.9965 309.9232 0010681 294.4110 130.3531 14.90330611 59
OBJECT B
1 43029U 17075B 17329.08445946 -.00000027 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9999
2 43029 35.0001 309.9444 0009487 286.3632 140.8123 14.90404942 40
OBJECT C
1 43030U 17075C 17329.08622319 -.00000027 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9992
2 43030 34.9948 309.9043 0010849 296.1554 140.5326 14.90422300 29
CZ-2C R / B
1 43031U 17075D 17329.08340975 -.00000053 00000-0 00000 + 0 0 9997
2 43031 35.2151 310.1448 0103082 55.9855 29.6258 15.12796120 42
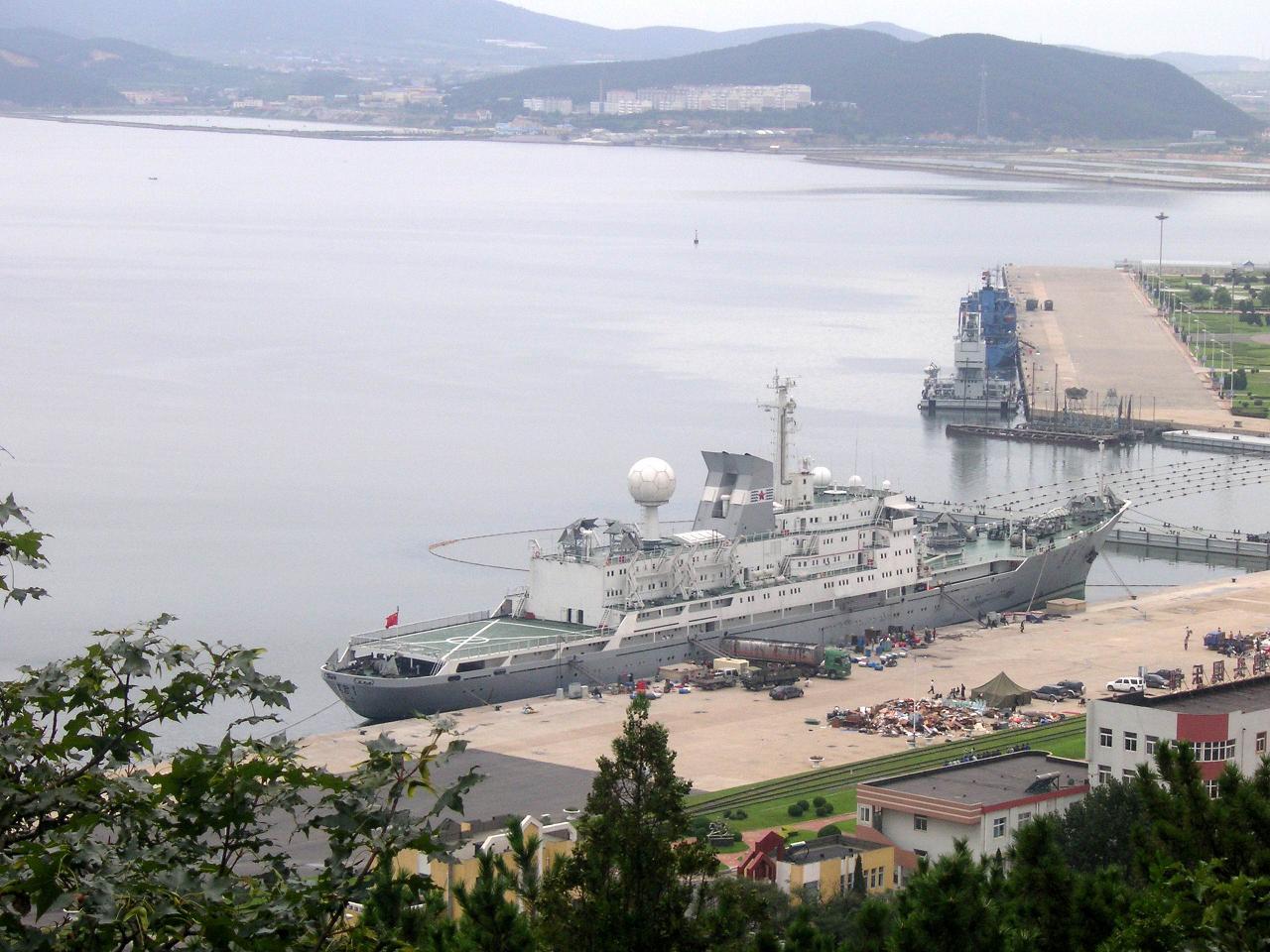
It should be noted that the
Yuan Wang 7 spacecraft and monitoring vessel , the newest of the Chinese BEMs, has been part of the orbiting of the South Pacific Ocean.
YG-30, a new Chinese NOSS-like
Just like
, this new satellite triplet is designed by the
Shanghai Engineering Center for Microsatellites , a fialiale of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. It should be noted that the SECM gave another name to these satellites,
Chuang Xin 5 (CX-5, 创新 5 号), which means "Innovation 5" in Chinese.
These would be ELINT reconnaissance satellites to determine the position of naval fleets by basing on their electromagnetic emissions, and to track the movements of these. But unlike the five constellations launched between 2010 and 2014, namely
YG-9 ,
YG-16 ,
YG-17 ,
YG-20 and
YG-25 , which are placed in 1,100 km × 1,100 km orbits × 63 °, the first two groups of YG-30 were put into lower orbits at about 600 km × 600 km × 35 °.
The low inclination of these new satellites suggests that they are rather dedicated to monitoring low latitude areas (N35 ° to S35 °), such as the Indian Ocean, the South China Sea and the Philippine Sea for example, and will increase the revisit period and thus improve the effectiveness of monitoring these priority areas.
The 3 orbital planes of JB-8
The three satellites of the constellation YG-30 Group 02 (Image: CCTV)
If we believe in
, two more YG-30 triplets will be launched before the next Chinese New Year, which will take place in February 2018. China will therefore have nine dedicated ELINT constellations to hunt for important marine targets, including aircraft carriers, in the four corners of the world's oceans.
These remote sensing capabilities are complemented by other Chinese optical and radar satellites for all-weather, all-weather coverage and redundant on the naval force projection tools of its "potential enemies" (see the excellent "
"written by Clément).
The objective is not only to monitor, but also to provide shooting parameters for the various anti-ship weapons developed for the Chinese army, such as anti-ship ballistic missiles (ASBM) with a range of up to 4,000 km Chinese coasts.
Historical statistics
This launch is the 14th Chinese space launch in 2017, the 43ᵉ for the CZ-2C launcher, and the 256ᵉ for the Long March launchers family.
For now, the Long March rockets of the group CASC total 245 successes and 11 failures, a success rate of 95.70%.
Here is the chart tracking all the Chinese space launches since the first in 1970, including those that are not made by Long March launchers -