You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
News on China's scientific and technological development.
- Thread starter Quickie
- Start date
The Storage Laboratory of the Department of Computer Science won the first place in the list of the top 500 supercomputing storage (IO500) in the world
Tsinghua News, June 2nd. On May 24th, the International Supercomputing Conference (ISC23) released a new international IO500 ranking list. The "Pengcheng Cloud Brain II" storage system developed by the Department of Computer Science and Pengcheng Laboratory won the Ranked No. 1 in the world in the Supercomputing Storage Top 500 (IO500) list. The "Pengcheng Cloud Brain II" storage system deploys the high-performance file system SuperFS independently developed by the storage laboratory of the Department of Computer Science, and achieved 210,000 points in the full-node test, creating a new world record. The core members involved in this work include teachers such as Lu Youyou and Shu Jiwu from the Department of Computer Science, and students such as Zeng Shaoxun, Guo Hao, and Yang Yitian. This achievement was guided and strongly supported by Academician Zheng Weimin, Professor Chen Wenguang, and Pengcheng Laboratory of the Department of Computer Science.
China's prowess in medicine is pretty new but growing rapidly.

Most of these are original inventions.

The US still has a commanding advantage in the world of pharma, but is the last stronghold they got. If you look at the Nature Index, China leads the US in all categories except biology. It will take time to pass the US but I believe it can happen within a decade if the momentum persists.

Most of these are original inventions.

The US still has a commanding advantage in the world of pharma, but is the last stronghold they got. If you look at the Nature Index, China leads the US in all categories except biology. It will take time to pass the US but I believe it can happen within a decade if the momentum persists.
One more successful effort by China to make its vast alkali land arable. A specific developed rapeseed variant significantly increases crop production in alkali soil. It can even reduce the salt concentration in the field.
6月2日,在江苏盐城东台市油菜“耐盐碱高产高油”技术模式观摩会现场传来喜讯,经中国作物学会油料作物专业委员会组织专家现场测产,采用耐盐耐密高产高油新品种和密植抗盐稳产新技术,东台市盐碱地200亩连片种植的油菜新品种“中油杂501”,密度高达6万株/亩,机收实产达323.87公斤/亩,亩产油量约163.17公斤,比当地油菜平均单产增加59.5%,比当地油菜平均亩产油量增加82.7%,创盐碱地油菜高产新纪录;种植油菜后土壤盐含量降至约1‰,是周边冬闲区盐含量的50%左右,是作物品种改良适应盐碱地种植的成功典范,为“以种适地”盐碱地治理和利用、保障食用油供给安全提供了可复制推广的综合技术解决方案。
6月2日,在江苏盐城东台市油菜“耐盐碱高产高油”技术模式观摩会现场传来喜讯,经中国作物学会油料作物专业委员会组织专家现场测产,采用耐盐耐密高产高油新品种和密植抗盐稳产新技术,东台市盐碱地200亩连片种植的油菜新品种“中油杂501”,密度高达6万株/亩,机收实产达323.87公斤/亩,亩产油量约163.17公斤,比当地油菜平均单产增加59.5%,比当地油菜平均亩产油量增加82.7%,创盐碱地油菜高产新纪录;种植油菜后土壤盐含量降至约1‰,是周边冬闲区盐含量的50%左右,是作物品种改良适应盐碱地种植的成功典范,为“以种适地”盐碱地治理和利用、保障食用油供给安全提供了可复制推广的综合技术解决方案。
Baidu made a breakthrough in using AI to help design mRNA vaccines.
Paper previewed:
News story:
这是中国科技企业首次以第一完成单位的身份在《Nature》杂志发表论文。鉴于论文对生物医学领域的重要性,Nature杂志在正式排版之前先将预览版快车道上线 (accelerated article preview),这也是AI应用于mRNA领域的首篇CNS主刊论文。
mRNA疫苗被公认为是遏制COVID-19的可行工具, 但mRNA疫苗和药物仍面临一些挑战。其中如何高效设计出稳定、成药性更好的mRNA序列,是mRNA疗法研究领域的难点之一。
百度运用自然语言处理中网格解析(Lattice Parsing)技术,对mRNA疫苗序列进行优化,提升疫苗稳定性和有效性。LinearDesign算法巧妙地将序列设计的海量计算简化为自然语言处理中的经典问题,让“大海捞针”变成了“按图索骥”。
Paper previewed:
Algorithm for Optimized mRNA Design Improves Stability and Immunogenicity
Abstract
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines are being used to contain COVID-19 (1, 2, 3), but still suffer from the critical limitation of mRNA instability and degradation, which is a major obstacle in the storage, distribution, and efficacy of the vaccine products (4). Previous work showed that increasing secondary structure lengthens mRNA half-life, which, together with optimal codons, improves protein expression (5). Therefore, a principled mRNA design algorithm must optimize both structural stability and codon usage. However, due to synonymous codons, the mRNA design space is prohibitively large (e.g., ~10632 candidates for the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein), which poses insurmountable computational challenges. Here we provide a simple and unexpected solution using a classical concept in computational linguistics, where finding the optimal mRNA sequence is akin to identifying the most likely sentence among similar sounding alternatives (6). Our algorithm LinearDesign takes only 11 minutes for the Spike protein, and can jointly optimize stability and codon usage. On both COVID-19 and varicella-zoster virus mRNA vaccines, LinearDesign substantially improves mRNA half-life and protein expression, and dramatically increases antibody titer by up to 128× in vivo, compared to the codon-optimization benchmark. This surprising result reveals the great potential of principled mRNA design, and enables the exploration of previously unreachable but highly stable and efficient designs. Our work is a timely tool not only for vaccines but also for mRNA medicine encoding all therapeutic proteins (e.g., monoclonal antibodies and anti-cancer drugs (7, 8)).News story:
中国科技企业首次突破!百度以第一完成单位登顶《Nature》正刊
国际顶级学术期刊《Nature》正刊发表了百度与合作单位在生物计算领域的重磅突破性成果——《Algorithm for Optimized mRNA Design Improves Stability and Immunogenicity》,提出mRNA序列优化算法LinearDesign。这是中国科技企业首次以第一完成单位的身份在《Nature》杂志发表论文。鉴于论文对生物医学领域的重要性,Nature杂志在正式排版之前先将预览版快车道上线 (accelerated article preview),这也是AI应用于mRNA领域的首篇CNS主刊论文。
mRNA疫苗被公认为是遏制COVID-19的可行工具, 但mRNA疫苗和药物仍面临一些挑战。其中如何高效设计出稳定、成药性更好的mRNA序列,是mRNA疗法研究领域的难点之一。
百度运用自然语言处理中网格解析(Lattice Parsing)技术,对mRNA疫苗序列进行优化,提升疫苗稳定性和有效性。LinearDesign算法巧妙地将序列设计的海量计算简化为自然语言处理中的经典问题,让“大海捞针”变成了“按图索骥”。
iPhone's 80 percent components/Parts manufactured in Mainland. unbelievable
so world's most valuable company is basically Chinese. LOL

people always talk about C919 have many western parts. but they just ignore how much Apple dependent on Chinese supply chain. same thing with other Global high tech firms. Siemens sourced 80 percent components/parts for their high end CT/MR scan machines from China. soon they will open second assembly line in Shenzhen.
so world's most valuable company is basically Chinese. LOL

people always talk about C919 have many western parts. but they just ignore how much Apple dependent on Chinese supply chain. same thing with other Global high tech firms. Siemens sourced 80 percent components/parts for their high end CT/MR scan machines from China. soon they will open second assembly line in Shenzhen.
China grows blood stem cells in space in what scientists say is first-of-its-kind experiment
- Cells cultivated on Tiangong space station’s lab module return to Earth, where they will continue to be tested and analysed, Chinese team says
- The work lays a solid foundation for further study of regenerative medicine in space, according to lead researcher
Published: 10:00pm, 5 Jun, 2023 Updated: 10:00pm, 5 Jun, 2023
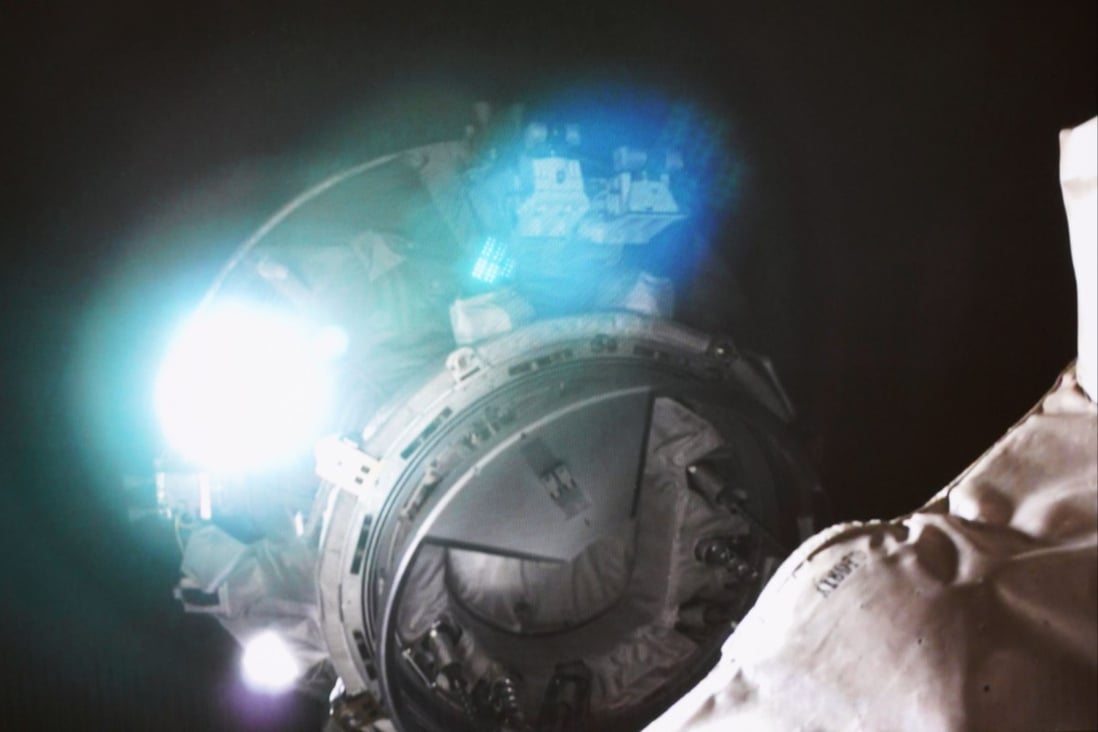

The stem cells were brought to China’s space station by the Tianzhou 6 cargo spacecraft on May 10. Photo: Xinhua
Chinese scientists say they have conducted a first-of-its-kind experiment to produce blood in space.
The stem cells were brought back to Earth by the Shenzhou 15 spacecraft on Sunday after being cultured for half a month in the of China’s .
Lei Xiaohua, a researcher with the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences who led the experiment, said his team would carry out testing and analysis of the cells.
After the completion of the experiment, China is expected to become the first country to create early-stage blood stem cells in space, Lei told China Science Daily on Sunday.
The cells were brought to China’s space station by the on May 10. The experiment was conducted after the Tianzhou 6 docked with the space station.
Lei’s team put human pluripotent stem cells – embryonic cells that can give rise to all major human cells – into the cell culture module on Tianzhou 6. After docking, the cells were placed in the biotechnology experiment cabinet in the .
The next step was to observe the pluripotent stem cells as they differentiated into blood stem cells.
A picture provided by Lei to state broadcaster CCTV showed the pluripotent stem cells starting to differentiate into blood stem cells while in space.
“These blood stem cells will undergo further maturation and differentiation to form a cluster of blood stem cells similar to a bunch of grapes,” Lei was quoted as saying by CCTV on Saturday.
“We have achieved the first goal of our experiment, which is to produce human blood stem cells in space,” he said.
“While in orbit, the stem cells were in good condition and the collected pictures were clear. The data collected was in line with our expectations.”
Lei added that the experiment would lay a solid foundation for further research on stem cell differentiation and regenerative medicine in space.
Scientists have been sending stem cells to space to test the effects of microgravity on cells.
In November, the University of San Diego Sanford Stem Cell Institute sent its blood stem cells to the International Space Station (ISS) to learn how human cells age in a zero-gravity environment.
In May, American scientists sent stem cells to space with Axiom Space’s Axiom Mission 2. Their experiment aims to examine whether scientists can cultivate induced pluripotent stem cells in microgravity.
Lei said scientists were interested in the research because pluripotent stem cells have unlimited growth potential and can differentiate into any type of cell in the body, making them an excellent source of cells for use in regenerative medicine.
Lei said his team also planned to conduct research on the growth of pluripotent stem cells in space with the Tianzhou 7 and Tianzhou 8 missions. China has not yet announced the schedule for future Tianzhou missions.
Before that, they will compare the blood stem cells produced in space with a control group grown on Earth to find the specific genes that affect the cells’ growth process in space, according to China Science Daily.