Maybe someone will be more interested in V6
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
News on China's scientific and technological development.
- Thread starter Quickie
- Start date
China’s latest brainwave? Controlling space robots using mind power
- A device that can be controlled by a user’s brain has achieved unprecedented accuracy in tests, scientists say
- It could be used at the Chinese space station to operate a giant robotic arm
in BeijingPublished: 10:00pm, 25 Mar, 2022
Updated: 10:56pm, 25 Mar, 2022

Chinese astronauts could soon be using mind power to operate a giant arm at their space station. Pictured is an artist’s interpretation of neuron pulses within a human brain. Photo: Shutterstock
A research team with China’s manned say they have developed technology that will allow astronauts to control robotic equipment using their brainwaves.
It could transform how astronauts operate the giant arm on the Chinese space station – a sophisticated piece of machinery with many flexible components.
The arm has so far been controlled by astronauts with a joystick and keyboard, which can sometimes be difficult in a weightless environment. Existing brain-control technology can control it with 40 to 80 per cent accuracy, which is below the standard needed in space – but a simulation of a new brain-computer interface has shown accuracy of above 99 per cent.
For comparison, the average accuracy of typing on a keyboard is only about 92 per cent.
The head-mounted device is said to be simple to use. “An untrained person can use it to issue commands with fairly high accuracy and speed,” said Professor Wang Congqing and his colleagues in a paper published last month in domestic peer-reviewed journal Computer Measurement and Control.
China was the first country to introduce brain control to space. During the Shenzhou 11 mission in 2016, Chinese astronauts Jing Haipeng and Chen Dong used a mind-reading device designed to aid their work.
Details of the experiment, conducted at the China Astronauts Research and Training Centre in Beijing, remained classified. But professor Huang Weifen, deputy chief designer of the system, told state media that experimental data suggested the technology had good potential.
“In future space exploration, humans and machines will work together,” she was quoted by state news agency Xinhua as saying. “A person no longer needs to use a keyboard, mouse or even joystick, but can use their brain and eyes.”
, will make use of brain-powered tech after its main structure is completed, which should be by the end of the year, according to the Chinese space authorities.
Human brain activity is extremely complex, and a major challenge to brain-controlled technology is the separation of useful signals from background noise.
A person wearing Wang’s device needs to look at an animated robotic arm on a computer screen. Each part of the arm blinks at a unique rate, and when the eyes focus on a blinking component, it stimulates the formation of brainwaves with the same frequency.
This allows the machine to read the mind – but the useful signals are rare, and most of them are weak.
To improve the device’s performance, Wang’s team used to help discover links between seemingly unrelated brainwave patterns to obtain additional information.
Thirty-five volunteers were enlisted to move or rotate a virtual robotic arm by thinking, with 11 of them completing the tasks without a hitch.
The average accuracy was 99.07 per cent, according to the researchers. It was marginally lower for the 27 volunteers who had no experience at all, still reaching 98.9 per cent.
The machine could recognise a command almost instantly. According to the researchers’ estimates, the “bandwidth” of information passed from the brain to the computer has reached 150 bytes per minute, nearly 10 times as much as was possible using the old approach.
It remained unclear when the technology would be used in space missions, but Wang’s team said that the device would soon be upgraded to handle more complex tasks and offer greater accuracy and speed.
Some Chinese factories have asked workers to wear a brain surveillance helmet to help them focus on their job and prevent work injuries.
Another study by Chinese researchers suggested that similar technology could enable industrial robots to work seamlessly with humans and speed up the operation of an assembly line.
In December, a research team with the National University of Defence Technology said they had developed a mind-reading helmet for Chinese soldiers. The futuristic helmet was designed for urban warfare, according to the researchers.
They said that it combined brain-control technology and augmented reality to help soldiers identify, track and eliminate enemies hidden in buildings.
The US Commerce Department’s industry and security bureau said last month that such technology would give China a cognitive advantage in the battlefield and threaten the national security of the United States.
150 bytes per minute?the “bandwidth” of information passed from the brain to the computer has reached 150 bytes per minute, nearly 10 times as much as was possible using the old approach.
The first step, to creating an EVA unit.
China’s latest brainwave? Controlling space robots using mind power
in Beijing
- A device that can be controlled by a user’s brain has achieved unprecedented accuracy in tests, scientists say
- It could be used at the Chinese space station to operate a giant robotic arm
Published: 10:00pm, 25 Mar, 2022
Updated: 10:56pm, 25 Mar, 2022

Chinese astronauts could soon be using mind power to operate a giant arm at their space station. Pictured is an artist’s interpretation of neuron pulses within a human brain. Photo: Shutterstock
A research team with China’s manned say they have developed technology that will allow astronauts to control robotic equipment using their brainwaves.
It could transform how astronauts operate the giant arm on the Chinese space station – a sophisticated piece of machinery with many flexible components.
The arm has so far been controlled by astronauts with a joystick and keyboard, which can sometimes be difficult in a weightless environment. Existing brain-control technology can control it with 40 to 80 per cent accuracy, which is below the standard needed in space – but a simulation of a new brain-computer interface has shown accuracy of above 99 per cent.
For comparison, the average accuracy of typing on a keyboard is only about 92 per cent.
The head-mounted device is said to be simple to use. “An untrained person can use it to issue commands with fairly high accuracy and speed,” said Professor Wang Congqing and his colleagues in a paper published last month in domestic peer-reviewed journal Computer Measurement and Control.
China was the first country to introduce brain control to space. During the Shenzhou 11 mission in 2016, Chinese astronauts Jing Haipeng and Chen Dong used a mind-reading device designed to aid their work.
Details of the experiment, conducted at the China Astronauts Research and Training Centre in Beijing, remained classified. But professor Huang Weifen, deputy chief designer of the system, told state media that experimental data suggested the technology had good potential.
“In future space exploration, humans and machines will work together,” she was quoted by state news agency Xinhua as saying. “A person no longer needs to use a keyboard, mouse or even joystick, but can use their brain and eyes.”
, will make use of brain-powered tech after its main structure is completed, which should be by the end of the year, according to the Chinese space authorities.
Human brain activity is extremely complex, and a major challenge to brain-controlled technology is the separation of useful signals from background noise.
A person wearing Wang’s device needs to look at an animated robotic arm on a computer screen. Each part of the arm blinks at a unique rate, and when the eyes focus on a blinking component, it stimulates the formation of brainwaves with the same frequency.
This allows the machine to read the mind – but the useful signals are rare, and most of them are weak.
To improve the device’s performance, Wang’s team used to help discover links between seemingly unrelated brainwave patterns to obtain additional information.
Thirty-five volunteers were enlisted to move or rotate a virtual robotic arm by thinking, with 11 of them completing the tasks without a hitch.
The average accuracy was 99.07 per cent, according to the researchers. It was marginally lower for the 27 volunteers who had no experience at all, still reaching 98.9 per cent.
The machine could recognise a command almost instantly. According to the researchers’ estimates, the “bandwidth” of information passed from the brain to the computer has reached 150 bytes per minute, nearly 10 times as much as was possible using the old approach.
It remained unclear when the technology would be used in space missions, but Wang’s team said that the device would soon be upgraded to handle more complex tasks and offer greater accuracy and speed.
Some Chinese factories have asked workers to wear a brain surveillance helmet to help them focus on their job and prevent work injuries.
Another study by Chinese researchers suggested that similar technology could enable industrial robots to work seamlessly with humans and speed up the operation of an assembly line.
In December, a research team with the National University of Defence Technology said they had developed a mind-reading helmet for Chinese soldiers. The futuristic helmet was designed for urban warfare, according to the researchers.
They said that it combined brain-control technology and augmented reality to help soldiers identify, track and eliminate enemies hidden in buildings.
The US Commerce Department’s industry and security bureau said last month that such technology would give China a cognitive advantage in the battlefield and threaten the national security of the United States.
Joking aside, there's a lot of applications with brain-controlled systems, opening a lot of possibilities that are difficult or unable to obtain before like treating neurological diseases and disability-aids. Or that, "cognitive advantage" US seems to think is a national security threat...
A demonstration project of Hualong One – China's domestically developed third-generation nuclear power technology – has been fully completed with officials saying the second of its two units is ready for commercial operation in southeast China's Fujian Province.
The second unit was connected to the grid two months ago and went through a comprehensive debug test in early February, according to its operator, China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC).
"It was examined during the Spring Festival and is in good condition now, and all its indicators meet the design requirements," Xu Jinlong, deputy general manager of CNNC's Fuqing nuclear power plant, said Friday.
The project's landmark first unit started commercial operation on January 30, 2021. It finished its first refueling and overhaul early this month monitored by China's National Nuclear Safety Administration.
CNNC said the annual electricity output of the two Hualong One reactors could be close to 20 billion kilowatt-hours, equal to that of 6.24 million tonnes of standard coal consumption and cutting more than 16.3 million tonnes of carbon emission.
The Hualong One technology, jointly developed by CNNC and China General Nuclear Power Corporation, has more than 700 patents and 120 software copyrights.
The reactor adopts both active and passive safety measures to prevent and contain potential accidents. It also has a double-layer shell that can withstand a 9-magnitude earthquake and even an air crash.
More than 20 countries and regions, including Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Argentina and Brazil have expressed a desire for cooperation with CNNC, the company said.
The Karachi nuclear power plant in Pakistan is the first overseas demonstration project of Hualong One. Its first unit has also started commercial operation and the second unit is connected to the grid.
China is developing its nuclear power based on strict safety standards with the aim of cutting carbon emissions.
By the end of last year, there were 53 running nuclear power units in the country, generating a total of 407 billion kWh of electricity in 2021, which accounted for about 5 percent of the country's total energy output in the year, according to data from China Nuclear Energy Association.

A demonstration project of Hualong One – China's domestically developed third-generation nuclear power technology – has been fully completed with officials saying the second of its two units is ready for commercial operation in southeast China's Fujian Province.
The second unit was connected to the grid two months ago and went through a comprehensive debug test in early February, according to its operator, China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC).
"It was examined during the Spring Festival and is in good condition now, and all its indicators meet the design requirements," Xu Jinlong, deputy general manager of CNNC's Fuqing nuclear power plant, said Friday.
The project's landmark first unit started commercial operation on January 30, 2021. It finished its first refueling and overhaul early this month monitored by China's National Nuclear Safety Administration.
CNNC said the annual electricity output of the two Hualong One reactors could be close to 20 billion kilowatt-hours, equal to that of 6.24 million tonnes of standard coal consumption and cutting more than 16.3 million tonnes of carbon emission.
The Hualong One technology, jointly developed by CNNC and China General Nuclear Power Corporation, has more than 700 patents and 120 software copyrights.
The reactor adopts both active and passive safety measures to prevent and contain potential accidents. It also has a double-layer shell that can withstand a 9-magnitude earthquake and even an air crash.
More than 20 countries and regions, including Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Argentina and Brazil have expressed a desire for cooperation with CNNC, the company said.
The Karachi nuclear power plant in Pakistan is the first overseas demonstration project of Hualong One. Its first unit has also started commercial operation and the second unit is connected to the grid.
China is developing its nuclear power based on strict safety standards with the aim of cutting carbon emissions.
By the end of last year, there were 53 running nuclear power units in the country, generating a total of 407 billion kWh of electricity in 2021, which accounted for about 5 percent of the country's total energy output in the year, according to data from China Nuclear Energy Association.
View attachment 85966
State-owned China National Nuclear Corp. (CNNC) has signed a contract with Nucleoeléctrica Argentina S.A. to build the Atucha III nuclear project using China's Hualong One technology in the South American country.
Look at the graph carefully. EU's share is recovering and increasing . Most likely due to scientists from eastern Europe and Russia. No institute in the world comes close to IAS , IHES and Bonn (all thanks to Peter Scholze).
USTC realizes chip-integrated cold-atom magneto-optical trap system for the first time
From the micro-net news, the team of Academician Guo Guangcan of China University of Science and Technology recently cooperated with Professor Lu Zhengtian to combine an independently designed magnetic field chip with a grating chip to realize a dual-chip cold-atom magneto-optical trap system, making new progress in chip-based cold-atom systems. .
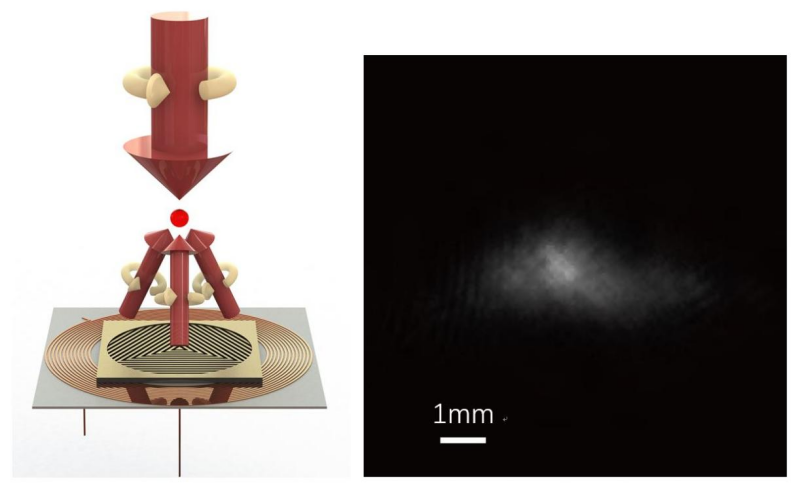
Image source: University of Science and Technology of China
It is reported that the magneto-optical trap based on the grating chip greatly simplifies the incident system of the six beams of space light in the traditional magneto-optical trap. It is small in size, light in weight, rich in optical windows and high in scalability. It is used in mobile quantum precision measurement systems, integrated There is great potential in quantum computing systems. However, for another important component of the magneto-optical trap, the magnetic field coil, we still can only use three-dimensional coil pairs to achieve it. If the size of the magnetic field coil is larger, thicker wires and stronger currents are required to achieve the learned magnetic field gradient, resulting in high power consumption and serious heat generation. If the size of the coil is reduced, the coil may severely obstruct the optical path, reducing the size of the available optical window.

