China’s Tianwen 1 Mars mission wins top international aerospace award
- Team recognised for making an ‘essential contribution to a deeper understanding of Mars and the solar system’
- It’s the second time a Chinese group has been granted the honour
in Beijing Updated: 9:30pm, 19 Sep, 2022
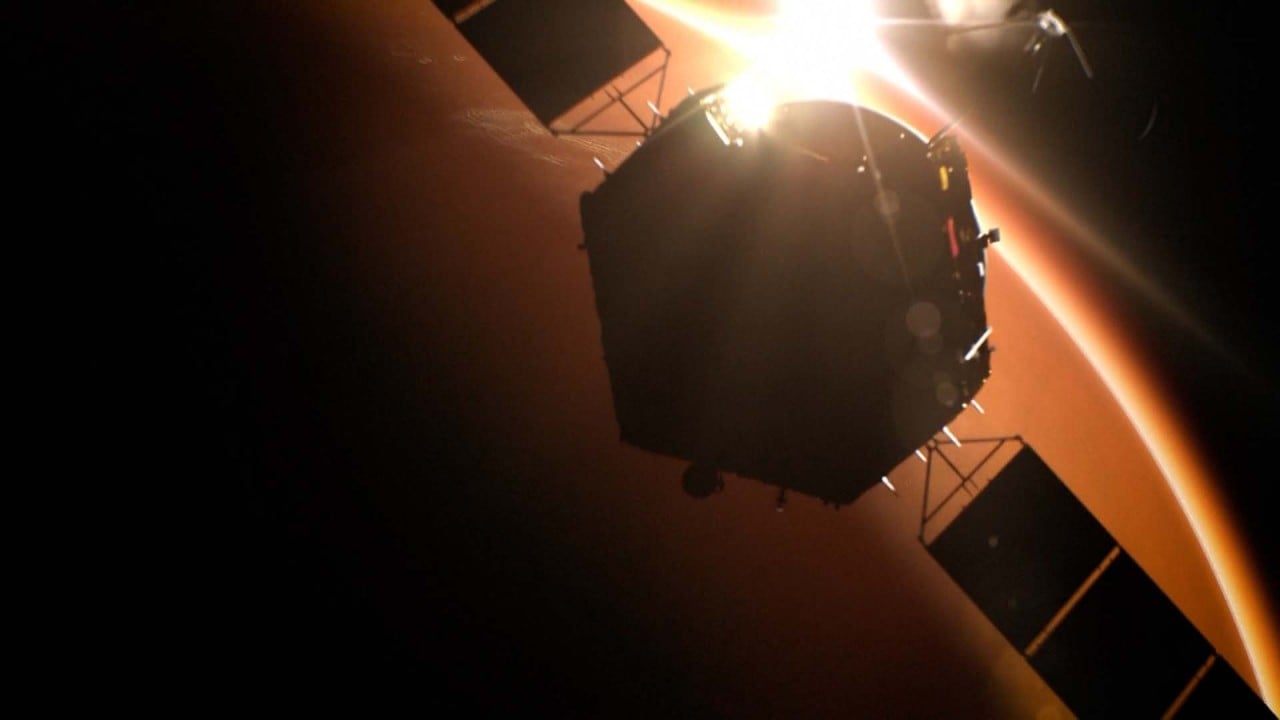
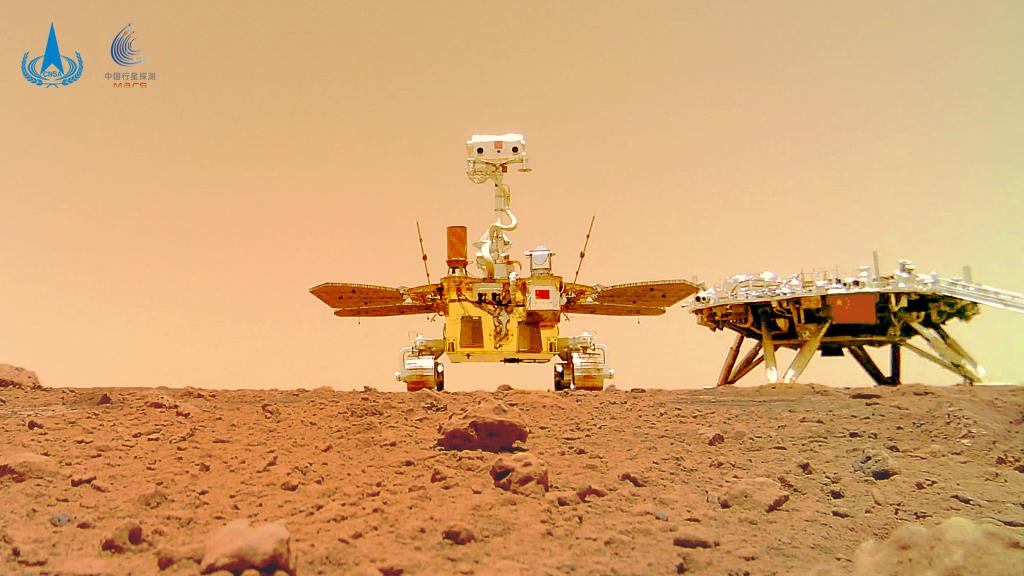
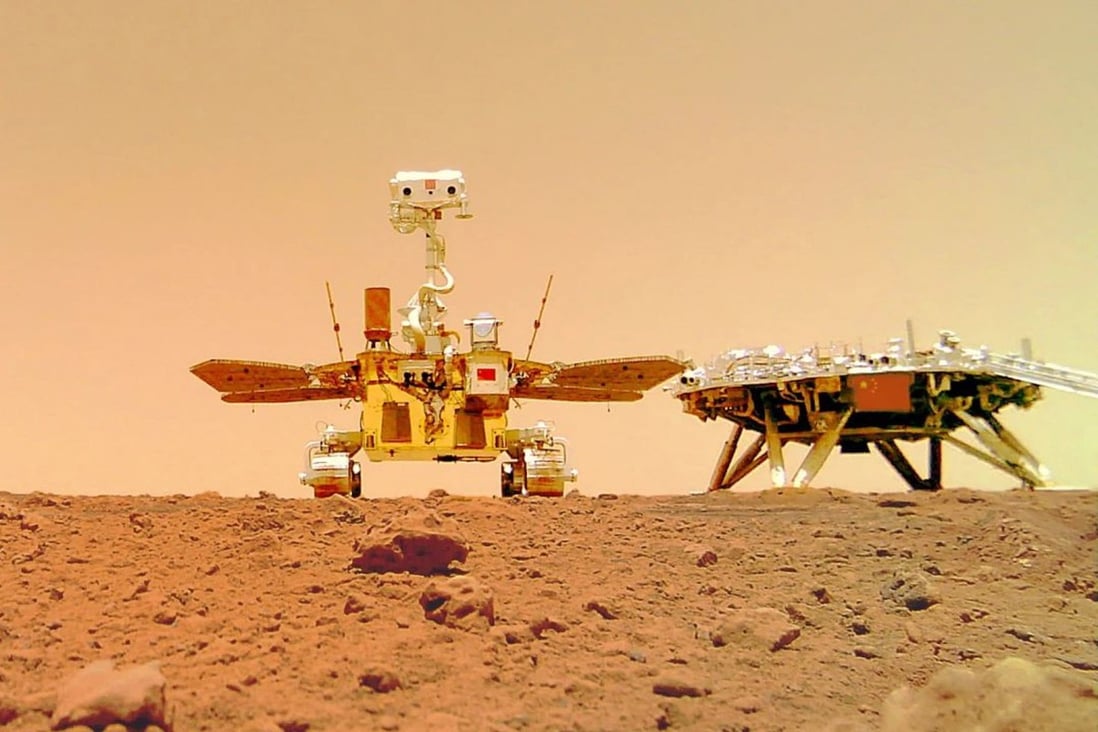
Tianwen 1 achieved orbiting, landing, and roving on Mars in one mission for the first time in history, according to the IAF. Photo: EPA-EFE
The team behind China’s
received the world’s highest aerospace award in Paris on Sunday.
The International Astronautical Federation (IAF) said the Tianwen 1 mission, which landed on the red planet last year, “offered an innovative option for successful Mars exploration and contributed to the advancement of deep space exploration technology”.
“Tianwen 1 achieved
, landing, and roving on Mars in one mission for the first time in history. The scientific data acquired during the mission made an essential contribution to a deeper understanding of Mars and the solar system,” the federation said.
Sun Zezhou, chief designer of the Tianwen 1 system, accepted the World Space Award on behalf of the team from IAF president Pascale Ehrenfreund at the International Astronautical Congress.
It is the second time a Chinese team has been given the award. Two years ago, scientists from the Chang’e 4 mission were recognised for leading the world’s first robotic spacecraft landing on the far side of the moon. Sun was also the chief designer of that probe.
By Thursday, the Tianwen 1 orbiter had been operating for more than 780 days, the mission’s Zhurong rover had travelled nearly 2km (1.2 miles) across the Martian surface and the mission had fully completed its exploration goals, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) said on Sunday.
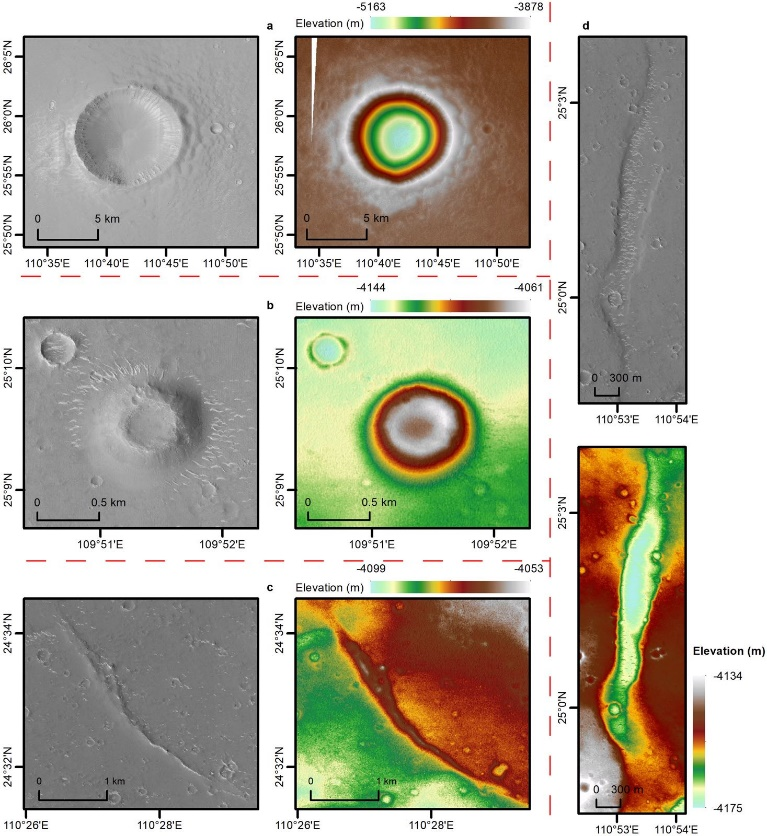
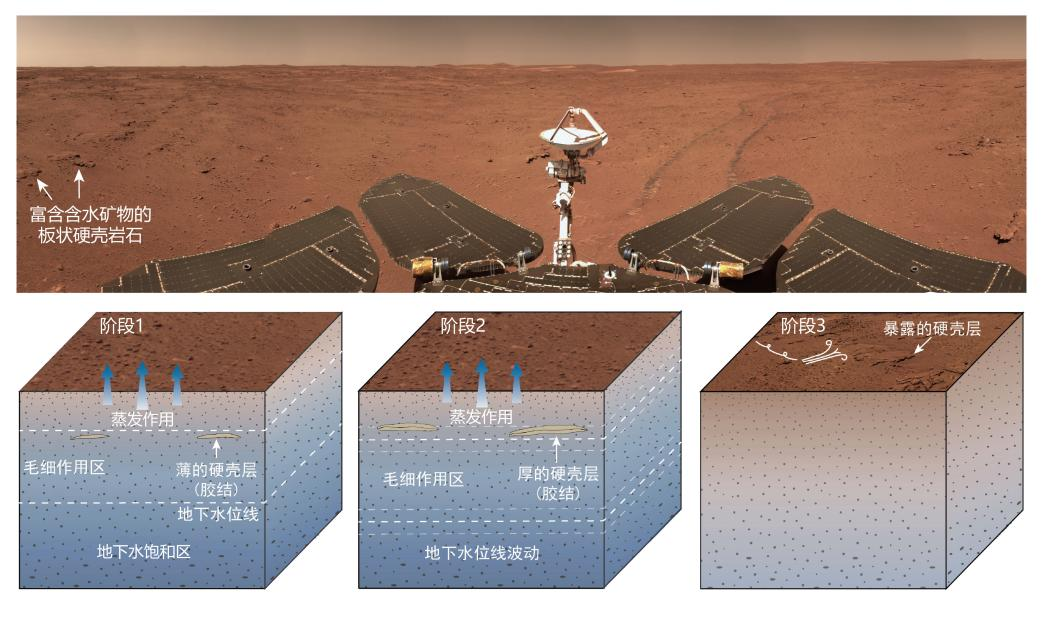
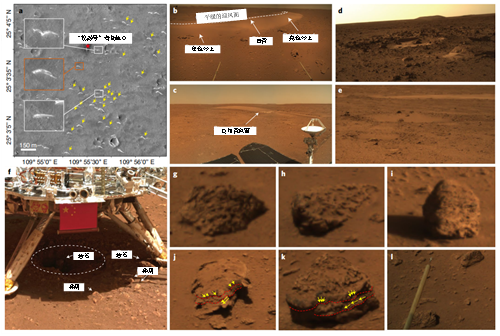
Among the first research results published so far, scientists said data and images of an area near the landing site pointed to
which is much more recent than previously thought.
The results of their search for water-bearing minerals on Utopia Planitia in the northern lowlands of Mars were reported in Science
Landing a spacecraft on the surface of Mars is one of the hardest things to do in planetary exploration. Due to the red planet’s low atmospheric pressure, the spacecraft needs to be slowed down around 7 minutes before touching the ground – and do so on its own because it is too far away to receive instructions from the Earth in time.
China and the United States are the only countries to have landed a spacecraft on Mars, and Tianwen 1’s touchdown prompted calls for collaboration between the space nations.
Asked in Paris about cooperation with China, Nasa administrator Bill Nelson reportedly said it was “up to China” and there needed to be openness and transparency from the Chinese side.
However, Nasa is not allowed to cooperate with China because of the Wolf Amendment, a US law that has been in place since 2011 to prevent the agency from working with Chinese commercial or government space agencies on a bilateral basis.
China does not have any law prohibiting cooperation with other spacefaring nations. Three European instruments went up on the Chang’e 4 mission and last week, the CNSA reached an agreement with the United Arab Emirates to help release their Rashid II rover during the Chang’e 7 mission to the moon’s southern polar region around 2026.
China and the US are pushing ahead with their own missions to
, possibly as early as 2031.
The IAF is a non-governmental organisation established in 1951 to promote and coordinate global space activities, with members from major space agencies, companies, and research institutions worldwide.
The federation launched the World Space Award in 2013 to recognise a “most eminent person or team” who has made “an exceptional impact” to the progress of the world space activities.