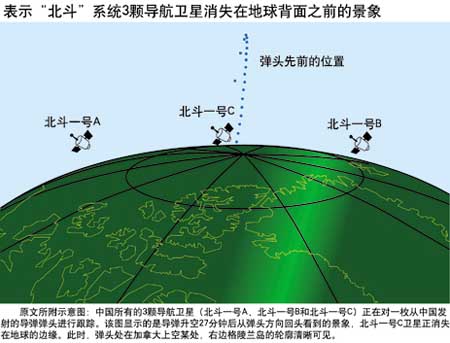
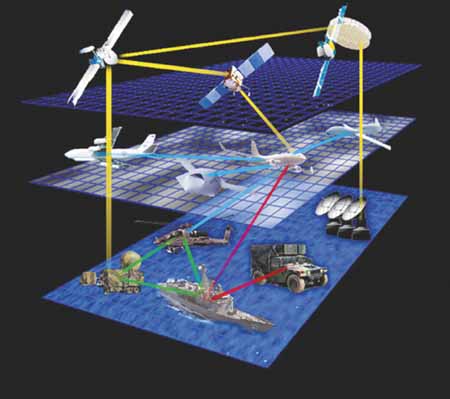
Vlad Plasmius
Junior Member
Re: When will China go to the moon?
Well, what are they gonna do? I believe it was Scott Adams who described how in his perfect society all but one of the guns in the world would be destroyed and that would be his gun. That way, if anyone wanted to question him they'd have to remember he has the only gun.
If anyone wants to question China or the U.S., they'll just cut them off from whatever their source is. Any nation powerful enough to be a threat would be highly dependant on foreign sources of energy. Any that aren't, well, they probably won't even care.
I don't know, we don't really have the same tenacity as China. Almost like we've lost our passion for space. I think China is more likely to end up there by the time they plan than we are. However, I imagine there won't be a very large gap in time. Russia may get up there pretty quick too. They have far more experience than China so it won't take them as long after deciding to go to the Moon. Europe will probably be last, though they also may get up there around the same time, don't know.
Exactly. Each would hand out to whoever they liked, but cut off those they don't. It would be under the pretext of giving it to everyone, but politicized and turned into a competition. China would try to win favor by using its energy sources, we'd try to do win favor with ours, and Russia would do the same.
Actually, our general lack of desire to cooperate with everyone has been the main reason for our development. Right now humanity has no real reason to develop except to show up the Joneses as it were. We first went to the moon because we wanted to rub it in the Soviets' noses. Now we want to beat the commies again, except now we have a reason to keep going after only a few visits.
No violation of UN law by a permanent member of the UNSC has been of as great as importance as the mining of resources in our Solar System. People won't do much about a country like Iraq being attacked, but they will over future means to sustain their own survival.
Well, what are they gonna do? I believe it was Scott Adams who described how in his perfect society all but one of the guns in the world would be destroyed and that would be his gun. That way, if anyone wanted to question him they'd have to remember he has the only gun.
If anyone wants to question China or the U.S., they'll just cut them off from whatever their source is. Any nation powerful enough to be a threat would be highly dependant on foreign sources of energy. Any that aren't, well, they probably won't even care.
Who's to say all three players will get there at the same time? It's much more realistic that a single power like the US will get there first and start operations. Then the others would start screaming and banging on the table like there was no tomorrow.
I don't know, we don't really have the same tenacity as China. Almost like we've lost our passion for space. I think China is more likely to end up there by the time they plan than we are. However, I imagine there won't be a very large gap in time. Russia may get up there pretty quick too. They have far more experience than China so it won't take them as long after deciding to go to the Moon. Europe will probably be last, though they also may get up there around the same time, don't know.
Besides, do you really think they'd work together to screw over everyone else? No way. They'd back their own allies against the others.
Exactly. Each would hand out to whoever they liked, but cut off those they don't. It would be under the pretext of giving it to everyone, but politicized and turned into a competition. China would try to win favor by using its energy sources, we'd try to do win favor with ours, and Russia would do the same.
Then humanity won't survive long, because without co-operation it will rip itself apart in the coming decades/centuries. Anyone who survived would have a pretty miserable existence. Perhaps the future would be brighter if people actively encouraged humanity working together, rather than just make jaded comments......
Actually, our general lack of desire to cooperate with everyone has been the main reason for our development. Right now humanity has no real reason to develop except to show up the Joneses as it were. We first went to the moon because we wanted to rub it in the Soviets' noses. Now we want to beat the commies again, except now we have a reason to keep going after only a few visits.