by78
General
radon
radon
The French built radon detector for the Chang'e-6 mission has been completed and will be shipped to China sometime next month. The instrument weighs about 4.5 kg.

radon
radon



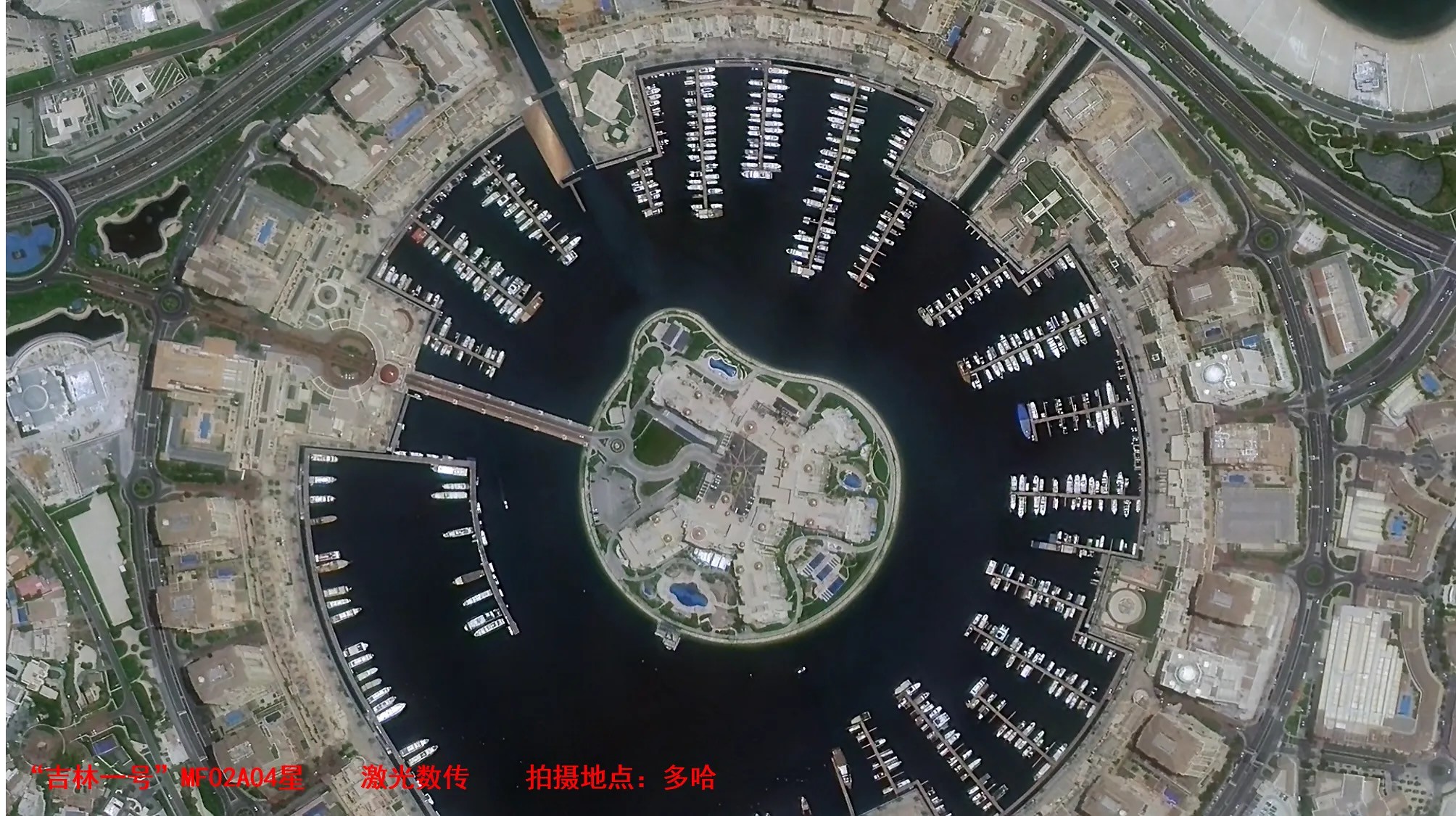
【吉林一号卫星完成我国首次业务化应用星地激光高速通信试验,通信速率10Gbps】为避免传统微波星地数传链路对“吉林一号”海量数据下传的限制,近期,长光卫星利用自研卫星“吉林一号”MF02A04星,与中国科学院空天信息创新研究院(空天院)部署的激光地面系统联合开展了星地激光高速通信试验并取得成功,标志着我国已成功实现星地激光高速通信的工程应用,为我国星地通信体制从微波拓展至激光奠定了坚实的基础。
长光卫星“吉林一号”MF02A04星总设计师陈善搏介绍,本次长光卫星联合空天院成功开展的星地激光通信试验,为国内首次面向业务化应用开展的超高速(10Gbps)星地激光通信试验,单次通信时长达100s以上。为避免姿控部件扰动对卫星载荷产生的影响,长光卫星突破了载荷-星敏感器微振动/热变形抑制等一系列关键核心技术,在确保光学载荷清晰成像的同时,高标准满足激光高指向精度及稳定度的要求。试验顺利下传的光学载荷图像数据经解析后质量良好,可以高标准满足业务化应用需求。
长光卫星星载激光通信技术负责人邢斯瑞介绍,长光卫星立足先进光学与卫星平台技术,联合北京融为科技有限公司研制了该套星地激光通信载荷,该载荷突破传统设计桎梏,与卫星平台采用一体化设计思路,突破载荷轻小型化设计、抗大气湍流自适应编码等关键技术,在复杂大气条件下实现星地10Gbps无误码数据传输。本次激光通信试验的成功,标志着星地数传技术正式由Gbps进入10Gbps时代,由微波数传进入微波、激光数传时代。下一步,长光卫星将联合项目团队,开展星地激光通信常态化、业务化试运行,为后续40Gbps星地激光通信载荷规模化应用提供技术基础。
长光卫星于2023年6月15日成功发射的“吉林一号”平台02A系列卫星也搭载了新一代激光通信载荷,用于在轨验证星间及星地高速通信技术,在实现星地通信的基础上,进一步完成高速星间激光通信任务。


The French built radon detector for the Chang'e-6 mission has been completed and will be shipped to China sometime next month. The instrument weighs about 4.5 kg.






An update on the , which is a joint project between the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the European Space Agency. An engineering prototype has passed various assessments, and the project is now moving onto the prototype stage. The final spacecraft is scheduled to be launched in April of 2025.
【SMILE卫星中欧联合任务级转正样设计通过评审,2025年由织女星-C火箭发射】6月26日至29日,太阳风-磁层相互作用全景成像卫星任务(Solar wind Magnetosphere Ionosphere Link Explorer,SMILE)中欧联合任务级转正样设计评审以现场和视频相结合的方式在上海顺利完成。
SMILE任务是中欧联合实施的空间科学卫星项目,双方于2015年5月一致同意SMILE任务入选中欧联合空间科学卫星任务。中国科学院于2016年11月批准SMILE任务中方工程立项。欧洲空间局于2019年3月批准SMILE任务欧方工程立项。
自中国科学院批准立项至今,中欧双方共完成了四个重大节点评审。2017年6月通过了任务确认评审,目的是固化工程设计方案和初步接口,明确研制基线,初步识别技术风险和进度风险,并评估工程研制计划是否合理可行。2018年10月通过了任务需求评审,目的是明确任务需求是否与科学目标相匹配、联合任务分析与设计是否满足功能和性能需求、研制计划是否满足任务要求。2020年1月通过了方案总结暨初样设计评审,SMILE任务转入初样研制阶段。2023年6月,在载荷级、整星级初样研制总结及正样设计通过评审的基础上,迎来了第四个重大节点评审——SMILE任务中欧联合转正样设计评审。
此次评审委员会主席为中国科学院国家空间科学中心主任、SMILE任务首席科学家王赤院士,SMILE任务工程总师叶培建院士,欧洲空间局监察长G. Colangelo.及未来任务部主任F. Safa。评审委员会由中欧双方研制团队代表及专家组成。
中欧双方于2023年4月开始准备评审文件,包括文档编写、更新及签署。5月完成了数据包的准备工作。6月2日,评审启动会正式召开,双方提交了评审数据包。联合评审委员组一共查找出200余条不一致项,其中重要不一致项近70条。6月26日至29日,评审委员会会议在上海召开,经过四天的讨论与咨询,评审委员会认为:所有不一致项均得到了有效处理并取得一致意见,待办事项有明确的闭环时间。SMILE卫星任务已按要求完成了初样阶段的研制工作;经测试和试验验证,初样各产品接口匹配,功能和性能指标满足任务要求;初样研制过程质量和技术状态受控。卫星及载荷按要求开展了正样设计,接口与技术状态明确,设计合理可行,功能和性能指标可满足任务要求;各大系统之间接口明确;正样研制技术流程、计划流程与质量控制点设置合理。
评审委员会一致同意中欧联合SMILE任务转正样设计通过评审。这是SMILE任务工程研制阶段的重要里程碑节点,标志着SMILE任务全面进入正样研制阶段。


DeepBlue Aerospace has inaugurated its new vertical engine test stand by completing a test run of its reusable engine.


An interview of the private launch provider Galactic Energy, conducted by Dongfan Four at the Paris Air Show. If you prefer reading to watching, of the interview. If you don't have time for either, here's a brief summary of the main points:
1) Six to eight launches are planned for Ceres-1 in the second half of this year, two of which will be sea launches from the Haiyang Spaceport (a.k.a Dongfeng Spaceport). The company is aiming for up to 20 launches of Ceres-1 between 2023 and 2024.
2) Maiden flight of Pallas-1 rocket is planned for the second half of 2024. Launch site not yet determined, with possible candidates being Wenchang or Taiyuan. The rocket is currently undergoing final assembly testing, and its engine (Cāngqióng/苍穹) continues to undergo test runs.
3) Pallas-1 will not be reusable in the beginning, but a reusable version is being actively developed, which will be necessary for the company's goals of providing space tourism in 10 years and astroid mining in 20 years.
4) The company hopes to provide launch services to the planned Xingwang internet constellation, which will have some 12,000 satellites.
5) A version of Pallas-1 with two strap-on boosters is on the roadmap, payload capacity to LEO will be 14 tons.

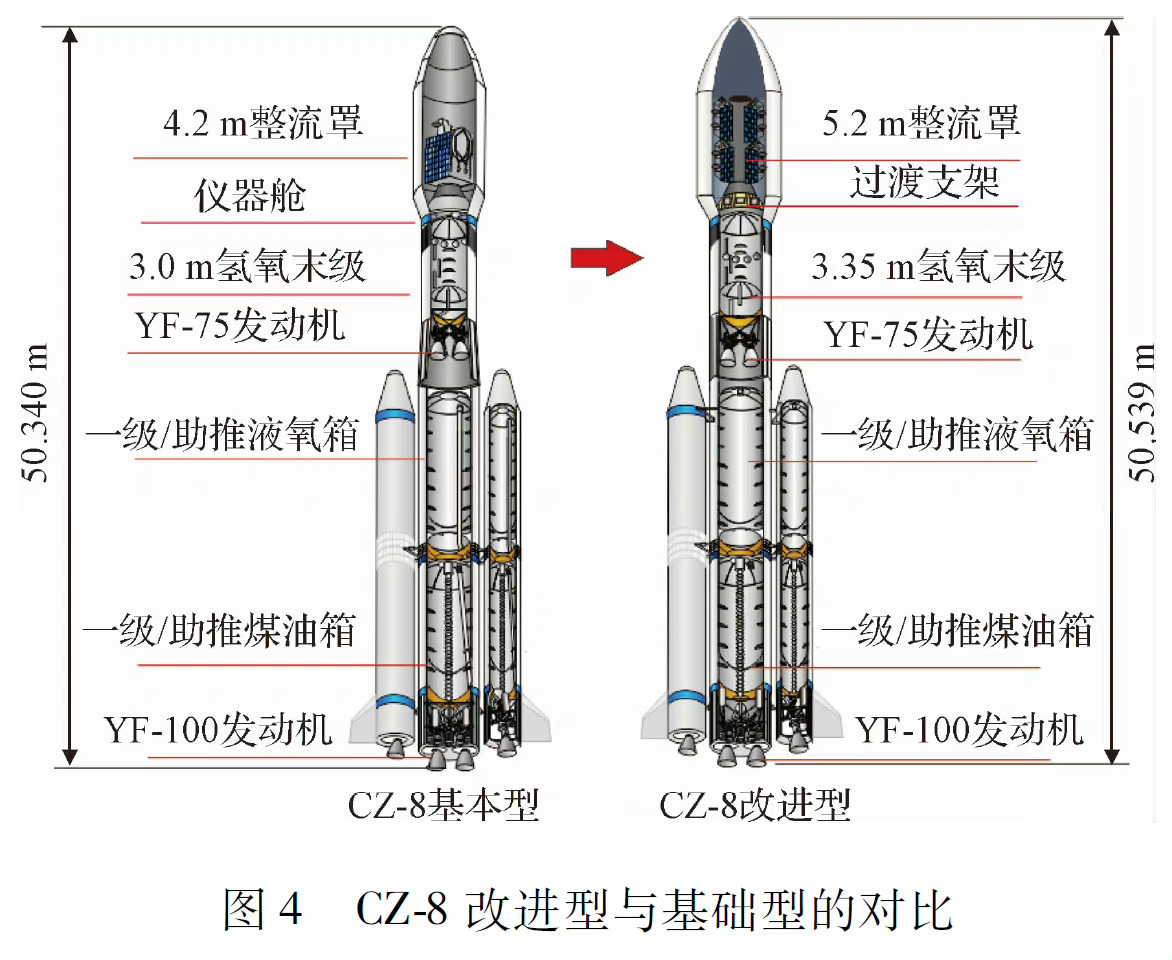
An that gives a good overview of the Long March 8 launch vehicle and its variants.
1) Long March 8 basic version:
- Length is 50.3m, takeoff mass is 358t, and takeoff thrust is 480t. Payload capacities to 700km SSO are 5.5 tons (with boosters) and 3 tons (without boosters).
- The basic version can meet the requirements of more than 90% of China's medium- and low-orbit launch missions.
2) Long March 8 improved version (LM-8G):
- LM8-G differs from the basic version by its larger payload fairing and a more powerful final stage. Its increased payload capacity meets the urgent launch needs of China's future communication, navigation, and remote sensing constellations.
- Take-off mass is 371 tons, take-off thrust is 480 tons, and payload capacity to 700km SSO is ≥6400kg.
3) "Three vertical" rapid launch turnaround for Hainan commercial spaceport (4th image):
- LM-8 will considerably improve launch turnaround time (7 to 10 days only), making it suitable for rapid commercial launches.
4) LM-8 will be assembled at a pulse production line, with an annual output of 50 rockets (last image).